New York, located in the northeastern region of the United States, is a state known for its iconic landmarks, vibrant culture, and stunning natural beauty. With its towering skyscrapers, picturesque countryside, and bustling urban centers, New York offers a unique blend of nature and culture. To help visitors and residents navigate this beautiful state, we have created a detailed map of New York with cities and highways.
This map highlights New York’s major cities, including New York City, Buffalo, Rochester, and Albany, as well as its primary highways and roads. Whether you’re planning a road trip or simply want to explore New York’s unique landscape and culture, this map is an essential tool. So, grab your map and get ready to discover all that New York has to offer, from its world-renowned museums to its charming small towns and everything in between.
Printable New York Map With Cities and Highways
Cities
Albany

Albany is the capital city of the U.S. state of New York and the seat of Albany County. Located on the west bank of the Hudson River, about 10 miles (16 km) south of its confluence with the Mohawk River, and about 135 miles (220 km) north of New York City, Albany is known for its architecture, commerce, culture, institutions of higher education, and rich history.
It is the economic and cultural core of the Capital District of the State of New York, which comprises the Albany–Schenectady–Troy Metropolitan Statistical Area, including the nearby cities and suburbs of Troy, Schenectady, and Saratoga Springs. With an estimated population of 1.1 million in 2013, the Capital District is the third most populous metropolitan region in the state.
Albany has a rich history dating back to the early 17th century when it was settled by Dutch colonists who built Fort Nassau for fur trading. The city officially became the capital of New York in 1797 and has since been a center of trade and transportation, as well as a hub for high-tech industries.
Albany’s population may have shrunk in the latter part of the 20th century, but it has since undergone a resurgence, with a significant building and renovation plan and the growth of its high-tech industry.
Amsterdam
Amsterdam is a city in Montgomery County, New York, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 18,219. The city is named after Amsterdam in the Netherlands and is surrounded on the northern, eastern, and western sides by the town of Amsterdam.
The city developed on both sides of the Mohawk River, with the majority located on the north bank. The Port Jackson area on the south side is also part of the city. Amsterdam has a rich history dating back to the colonial period when it was originally settled by the Dutch. The city played an important role in the American Revolution and was home to several notable figures, including General Nicholas Herkimer.
Today, Amsterdam is a vibrant community with a diverse population and a thriving downtown area. The city is home to several parks, museums, and cultural institutions, including the Walter Elwood Museum and the Mohawk Valley Gateway Overlook. With its rich history and cultural offerings, Amsterdam is a popular destination for visitors and residents alike.
Batavia
Batavia is a city in and the county seat of Genesee County, New York, United States. It is located near the center of the county, surrounded by the Town of Batavia, which is a separate municipality. The city’s population as of the 2020 census was 15,600.
The name Batavia honors early Dutch land developers and is Latin for the Betuwe region of the Netherlands. Batavia has a rich history dating back to the early 19th century when it was first settled. Today, the city is known for its economic development and was ranked third among the nation’s micropolitans in 2006 by Site Selection magazine.
The New York State Thruway (Interstate 90) passes north of the city, and the Genesee County Airport (GVQ) is also located north of the city. Batavia is home to the Batavia Muckdogs baseball team of the Perfect Game Collegiate Baseball League, who won the 2008 New York Penn League Championship. With its bustling economy and varied cultural offerings, Batavia is a great spot for visitors and residents.
Binghamton

Binghamton is a city in the U.S. state of New York and serves as the county seat of Broome County. Surrounded by rolling hills, it lies in the state’s Southern Tier region near the Pennsylvania border, in a bowl-shaped valley at the confluence of the Susquehanna and Chenango Rivers.
Binghamton is the principal city and cultural center of the Binghamton metropolitan area, home to a quarter-million people. The city has a rich history as a transportation crossroads and a manufacturing center, with a sustained economic prosperity that earned it the moniker of the Valley of Opportunity.
While the region lost a large part of its manufacturing industry in the late 20th century, Binghamton is now emerging as a healthcare- and education-focused city, with Binghamton University acting as much of the driving force behind this revitalization. Today, the city is known for its high-tech firms, healthcare institutions, and educational opportunities, attracting visitors from across the area.
Buffalo

Buffalo is the second-most populated city in the U.S. state of New York and the seat of Erie County. It lies in Western New York, at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of the Niagara River, on the United States border with Canada. With a population of 278,349 according to the 2020 census, Buffalo is the 78th-largest city in the United States.
Buffalo and the city of Niagara Falls together make up the two-county Buffalo–Niagara Falls Metropolitan Statistical Area, which had an estimated population of 1.2 million in 2020, making it the 49th largest MSA in the United States. Buffalo has a rich history dating back to the early 17th century when the French first explored the region.
The city’s growth was stimulated by the Erie Canal, which led to its incorporation in 1832 and made it the primary inland port between the Great Lakes and the Atlantic Ocean. Buffalo was also a major railway hub during the mid-19th century and was dominated by steel production.
Today, the city’s economy has diversified to include service industries such as healthcare, retail, tourism, logistics, and education, while retaining some manufacturing. Buffalo is also known for its cultural landmarks, educational institutions, and major-league sports teams. With its fascinating heritage and diverse offerings, Buffalo is a wonderful option for residents and tourists alike.
Dunkirk

Dunkirk is a city in Chautauqua County, New York, United States. It was settled around 1805 and incorporated in 1880. The population was 12,743 as of the 2020 census. Dunkirk is bordered on the north by Lake Erie, making it a popular destination for water sports and outdoor recreation.
The city shares a border with the village of Fredonia to the south and with the town of Dunkirk to the east and west. Dunkirk is the westernmost city in the state of New York and has a rich history dating back to its early settlement.
Today, the city is known for its beautiful waterfront and scenic views of Lake Erie. Dunkirk is also a hub for commerce and industry, with several major companies operating in the area. With its rich history and natural beauty, Dunkirk is a great spot to live, work, and play
Elmira

Elmira is a city and the county seat of Chemung County, New York, United States. It is the principal city of the Elmira, New York, metropolitan statistical area, which encompasses Chemung County. The population was 26,523 at the 2020 census, down from 29,200 at the 2010 census, a decline of more than 7 percent.
The City of Elmira is located in the south-central part of the county, surrounded on three sides by the Town of Elmira. It is situated in the Southern Tier of New York, a short distance north of the Pennsylvania state line. Elmira has a rich history dating back to the early 19th century when it was first settled.
The city played an important role in the Underground Railroad, with several safe houses and abolitionists located in the area. Today, Elmira is known for its cultural landmarks, including the Arnot Art Museum and the Clemens Center, which hosts a variety of performances and events throughout the year.
The city is also home to several parks, including Eldridge Park, which features a carousel and other attractions. Elmira is full of culture, heritage, friendly locals, and wonderful natural scenery.
Fredonia

Fredonia is a village in Chautauqua County, New York, United States. The population was 9,871 as of the 2020 census. Fredonia is located in the town of Pomfret, south of Lake Erie. The village is home to the State University of New York at Fredonia, which is located in the northwest part of the village.
Fredonia has a rich history dating back to its early settlement in the early 19th century. Today, the village is known for its charming downtown area, which features a variety of shops, restaurants, and cultural landmarks.
Fredonia is also one of only twelve villages in New York still incorporated under a charter, the other villages having incorporated or re-incorporated under the provisions of Village Law. With its rich history and cultural offerings, Fredonia is a popular destination for visitors and residents alike.
Freeport

Freeport is a village in the town of Hempstead, in Nassau County, on the South Shore of Long Island, in New York state. The population was 43,713 at the 2010 census, making it the second-largest village in New York by population. Freeport has a rich history dating back to the 1640s when it was first settled.
It was once an oystering community and later a resort popular with the New York City theater community. Today, Freeport is primarily a bedroom suburb, but it retains a modest commercial waterfront and some light industry.
The village is known for its beautiful waterfront, which offers a variety of recreational activities such as boating, fishing, and swimming. Freeport is also home to several parks and nature preserves, including Cow Meadow Park and Preserve and the Norman J. Levy Park and Preserve.
Fulton

Fulton is a city located in the western part of Oswego County, New York, United States. The population was 11,896 as of the 2010 census. The city is named after Robert Fulton, the inventor of the steamboat. Fulton has a rich history dating back to its early settlement in the 19th century.
The city played an important role in the development of the steamboat industry, with several companies operating in the area. Today, Fulton is known for its charming downtown area, which features a variety of shops, restaurants, and cultural landmarks.
The city is home to several parks, including Recreation Park, which offers a variety of recreational activities such as baseball, basketball, and tennis. Fulton is also home to the Oswego County Airport, which provides air travel options for residents and visitors. With its absorbing history and natural landscapes, Fulton is a great local destination.
Geneva

Geneva is a city located in Ontario and Seneca counties in the U.S. state of New York. It is situated at the northern end of Seneca Lake, with all land portions of the city located within Ontario County and the water portions in Seneca County. The population was 13,261 at the 2010 census. The city is supposedly named after the city and canton of Geneva in Switzerland.
The main settlement of the Seneca was spelled Zoneshio by early European settlers and was described as being two miles north of Seneca Lake. Geneva has a rich history dating back to the early 19th century when it was first settled. Today, the city is known for its beautiful waterfront and scenic views of Seneca Lake.
Geneva is also recognized as the “Lake Trout Capital of the World,” with several fishing tournaments and events held in the area each year. The city is home to several parks, including Seneca Lake State Park and Lakefront Park, which offer a variety of recreational activities such as hiking, boating, and swimming.
Glens Falls

Glens Falls is a city located in Warren County, New York, United States, and is the central city of the Glens Falls Metropolitan Statistical Area. The population was 14,830 at the 2020 census. The name was given by Colonel Johannes Glen, with the falls referring to a large waterfall in the Hudson River at the southern end of the city.
Glens Falls is situated in the southeastern corner of Warren County, surrounded by the town of Queensbury to the north, east, and west, and by the Hudson River and Saratoga County to the south. The city is known as “Hometown U.S.A.”, a title Look magazine gave it in 1944, and has also referred to itself as the “Empire City.”
In July 2023, for the second year in a row, Glens Falls was named the safest city in the USA, making it a popular destination for families and retirees. The city is home to several parks, including Crandall Park, which features a variety of recreational activities such as hiking, swimming, and picnicking. With its pleasing heritage and reputation for safety, Glens Falls is a satisfying place for a visit or to find your new home.
Ithaca

Ithaca is a city and the county seat of Tompkins County, New York, United States. Situated on the southern shore of Cayuga Lake in the Finger Lakes region of New York, Ithaca is the largest community in the Ithaca metropolitan statistical area. The city is named after the Greek island of Ithaca.
Ithaca is known as a college town, with Cornell University, an Ivy League university routinely ranked among the world’s best universities, and Ithaca College both located in the city. Nearby in Dryden, New York is Tompkins Cortland Community College (TC3). These three colleges bring thousands of students to the area, who increase Ithaca’s seasonal population during the school year.
As of 2020, the city’s population was 32,108. Ithaca is also known for its natural beauty, with several parks and nature preserves located in the area, including Buttermilk Falls State Park and Robert H. Treman State Park. With its reputation for academic excellence and natural beauty, Ithaca will reward your time if you choose to visit.
Jamestown

Jamestown is a city located in southern Chautauqua County, New York, United States. The population was 28,712 at the 2020 census, making it the largest city in the county. Situated between Lake Erie to the north and the Allegheny National Forest to the south, Jamestown is known for its natural beauty and outdoor recreational opportunities.
Nearby Chautauqua Lake is a freshwater resource used by fishermen, boaters, and naturalists. In the 20th century, Jamestown was a thriving industrial area, noted for producing several well-known products. The city was once called the “Furniture Capital of the World” because of the once-thriving furniture industry.
For most of the 20th century, Blackstone Corporation was Jamestown’s largest employer and one of the driving forces of the local economy, manufacturing washing machines and automobile components. Jamestown has also produced several notable individuals, including legendary comedienne Lucille Ball, U.S. Supreme Court justice and Nuremberg chief prosecutor Robert H. Jackson, and NFL Commissioner Roger Goodell.
Kingston

Kingston is the only city in, and the county seat of, Ulster County, New York, United States. The city is located 91 miles (146 km) north of New York City and 59 miles (95 km) south of Albany. The city’s metropolitan area is grouped with the New York metropolitan area around Manhattan by the United States Census Bureau.
The population was 24,069 at the 2020 United States Census. Kingston has a rich history dating back to the American Revolutionary War when it became New York’s first capital in 1777. During the war, the city was burned by the British on October 13, 1777, after the Battles of Saratoga.
In the 19th century, Kingston became an important transport hub after the discovery of natural cement in the region, with connections to other markets through both railroad and canal connections.
Today, many of the older buildings in Kingston are considered contributing as part of three historic districts, including the Stockade District uptown, the Midtown Neighborhood Broadway Corridor, and the Rondout-West Strand Historic District downtown. Each district is listed on the National Register of Historic Places, making Kingston a popular destination for history buffs and architecture enthusiasts.
Lackawanna
Lackawanna is a city located in Erie County, New York, United States, just south of the city of Buffalo in western New York State. The population was 19,949 at the 2020 census, making it one of the fastest-growing cities in New York, with a population growth of 10% from 2010 to 2020. Lackawanna is part of the Buffalo-Niagara Falls metropolitan area and is situated in the southwestern part of Erie County.
The town’s name derives from the Lackawanna Steel Company, which owned the steel plant around which the city developed. During the early 20th century, the Lackawanna steel plant was the largest in the world. The word “Lackawanna” refers to the steel company’s original location in the river valley of the same name, in eastern Pennsylvania.
That place name, in turn, might come from Lenape lèkaohane, meaning “sandy stream”, or lechauhanne, [lɛxaohánɛk], meaning “forks of the river”. With its rich industrial history and growing population, Lackawanna is a city on the rise in western New York State.
Lancaster

Lancaster is a town located in Erie County, New York, United States, centered 14 miles east of downtown Buffalo. Lancaster is an outer ring suburb of Buffalo and is known for its quiet neighborhoods and family-friendly atmosphere. As of the 2020 Census, the town population was 45,106, making it one of the larger towns in the area.
Located within the town is the village of Lancaster and the eastern half of the village of Depew. Depew’s western half lies within the town of Cheektowaga. The town is known for its excellent schools, with the Lancaster Central School District consistently ranked among the best in the state.
Lancaster is also home to several parks and recreational areas, including Como Lake Park and Westwood Park, which offer a variety of outdoor activities such as hiking, fishing, and picnicking. With its close proximity to Buffalo and its reputation as a family-friendly community, Lancaster is a popular destination for those looking to settle down in western New York.
Lockport

Lockport is a unique city located in Niagara County, New York, United States. It is both a city and the town that surrounds it, with the city serving as the Niagara County seat. The city has a population of 21,165 according to 2010 census figures, and an estimated population of 20,305 as of 2019.
Lockport is known for its historic Erie Canal locks, specifically Lock Numbers 34 and 35, which were built to allow canal barges to traverse the 60-foot natural drop of the Niagara Escarpment. The locks are a popular tourist destination, with visitors coming from all over to see this engineering marvel of the 19th century.
Lockport is also part of the Buffalo-Niagara Falls metropolitan area, making it a convenient location for those looking to explore western New York. With its rich history and unique attractions, Lockport is a must-visit destination for anyone traveling through Niagara County.
Long Beach

Long Beach is a beautiful oceanfront city located in Nassau County, New York, United States. It takes up a central section of the Long Beach Barrier Island, which is the westernmost of the outer barrier islands off Long Island’s South Shore. As of the 2020 Census, the city’s population was 35,029, up from the 2019 estimate of 33,454.
Long Beach was incorporated in 1922 and is nicknamed “The City by the Sea” (the Latin form, Civitas ad mare, is the city’s motto). The Long Beach Barrier Island is surrounded by Reynolds Channel to the north, east, and west, and the Atlantic Ocean to the south.
In 2022, Long Beach was named the best East Coast town for a summer getaway by Time Out magazine, making it a popular destination for tourists looking to enjoy the beach, boardwalk, and other outdoor attractions. With its stunning ocean views and vibrant community, Long Beach is an unmissable spot for anyone traveling to Nassau County.
New York
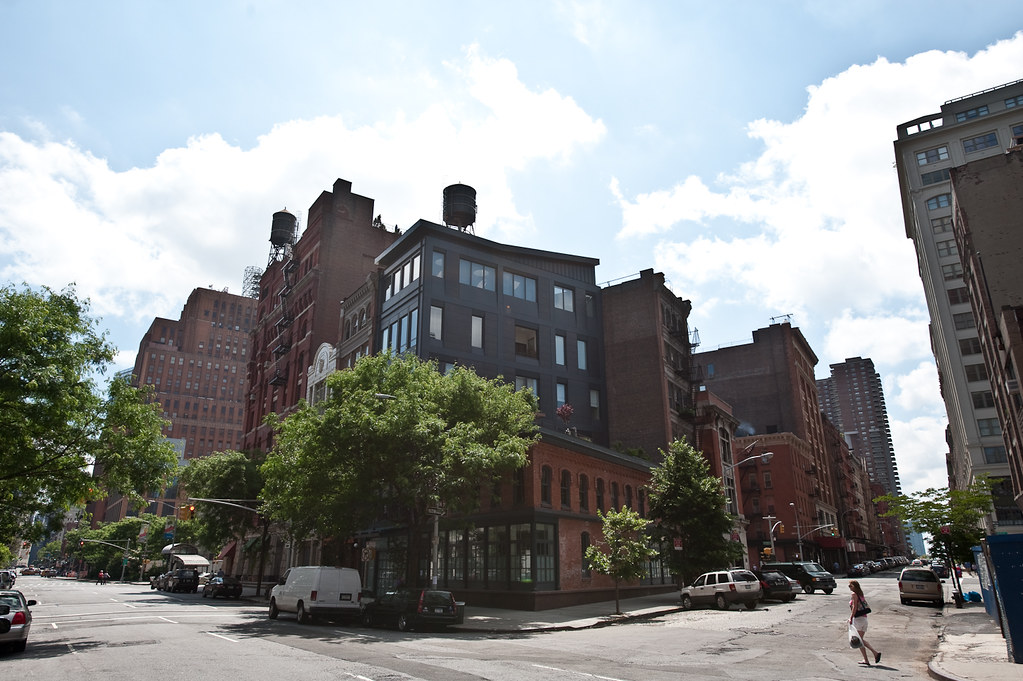

New York, often referred to as New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a population of 8,804,190 distributed over 300.46 square miles, the city is the most densely populated major city in the United States. New York City is situated on one of the world’s largest natural harbors and is at the southern tip of New York State.
The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive with a respective county. These five boroughs are Brooklyn (Kings County), Queens (Queens County), Manhattan (New York County), the Bronx (Bronx County), and Staten Island (Richmond County). New York City is a global city and is known for its cultural, financial, high-tech, entertainment, and media centers. It is home to the headquarters of the United Nations and is an important center for international diplomacy.
The city is the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the U.S. by both population and urban area. With a metropolitan statistical area population of over 20.1 million people and a combined statistical area population of 23.5 million, New York City is one of the world’s most populous megacities.
The city is also known for its linguistic diversity, with as many as 800 languages spoken in New York, making it the most linguistically diverse city in the world. The city is a hub for international finance, and its stock exchanges, the New York Stock Exchange and Nasdaq, are the world’s two largest by market capitalization of their listed companies.
New York City is also home to many of the world’s billionaires, individuals of ultra-high net worth, and millionaires. The city is a major center for the arts, education, and media and has been called a symbol of freedom and cultural diversity.
Niagara Falls

Niagara Falls is a city located in Niagara County, New York, United States. As of the 2020 census, the city had a total population of 48,671. It is situated adjacent to the Niagara River, across from the city of Niagara Falls, Ontario, and is named after the world-famous Niagara Falls that they share. The city is within the Buffalo-Niagara Falls metropolitan area and the Western New York region.
Niagara Falls has a rich history, with Europeans who migrated to the area in the mid-17th century opening businesses and developing infrastructure. In the 18th and 19th centuries, scientists and businessmen began harnessing the power of the Niagara River for electricity, attracting manufacturers and other businesses drawn by the promise of inexpensive hydroelectric power.
Despite an economic decline in the region following an attempt at urban renewal in the 1960s, Niagara Falls State Park and the downtown area closest to the falls continue to thrive as a result of tourism. However, the population has declined from a peak of 102,394 in the 1960s due to the loss of manufacturing jobs in the area. Niagara Falls remains an inspirational destination for anyone traveling to Western New York, with its astounding natural beauty and rich heritage.
Oswego

Oswego is a city located in Oswego County, New York, United States, with a population of 16,921 as of the 2020 census. The city is situated on Lake Ontario in Upstate New York, approximately 35 miles northwest of Syracuse.
Oswego promotes itself as “The Port City of Central New York” and serves as the county seat of Oswego County. It is bordered by the towns of Oswego, Minetto, and Scriba to the west, south, and east, respectively, and by Lake Ontario to the north.
Oswego Speedway, a nationally known automobile racing facility, is located in the city. The State University of New York at Oswego is also located just outside the city on Lake Ontario. Oswego is a beautiful city with a deep history and a buzzing community.
Plattsburgh
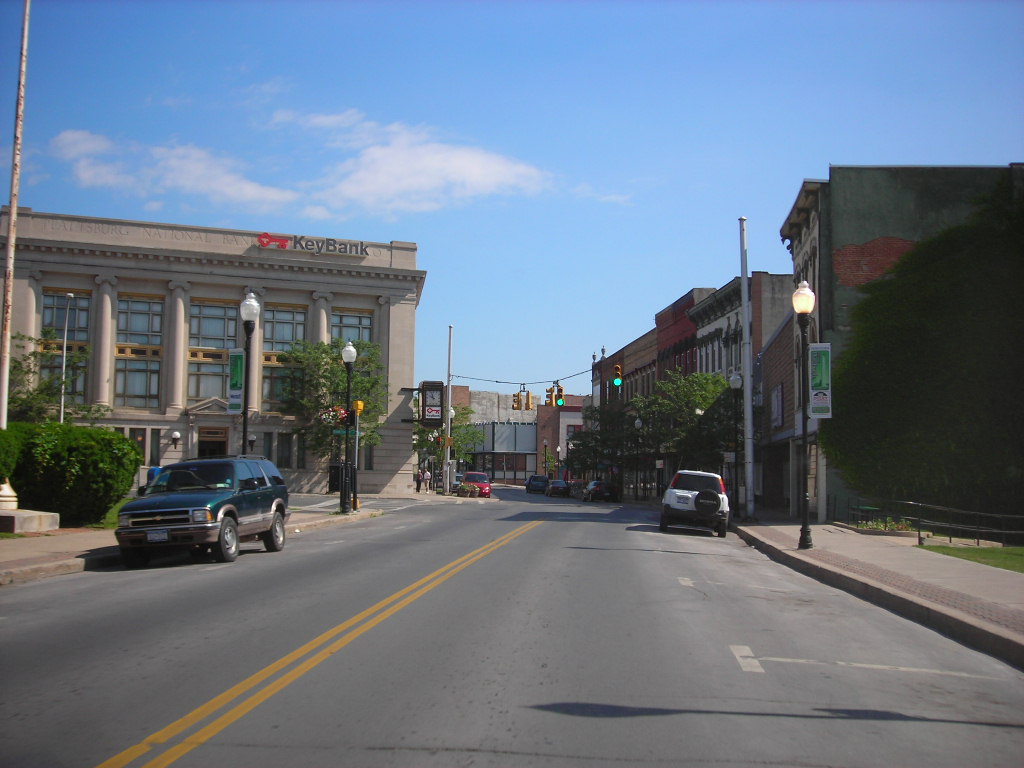

Plattsburgh is a city located in Clinton County, New York, United States, and serves as the county seat. With a population of 19,841 as of the 2020 census, Plattsburgh is situated on the northwestern shore of Lake Champlain. The surrounding Town of Plattsburgh had a population of 11,886 as of the 2020 census, making the combined population for all of greater Plattsburgh 31,727.
The city lies just to the northeast of Adirondack Park, immediately outside of the park boundaries, and serves as the main commercial hub for the sparsely populated northern Adirondack Mountains. The land around Plattsburgh was previously inhabited by the Iroquois, Western Abenaki, Mohican, and Mohawk people, and was claimed as a part of New France by Samuel de Champlain in 1609.
Plattsburgh has a rich history as an important military outpost, including serving as the site of the amphibious Battle of Plattsburgh in the War of 1812 and hosting one of the largest Citizens’ Military Training Camps prior to World War I. Today, Plattsburgh serves as a hub for economic development in the region and has been named one of the Financial Times Top 10 Micro City of the Future several times.
Port Chester
Port Chester is a village located in Westchester County, New York, and is the largest part of the town of Rye by population. With a population of 28,967 as of the 2010 U.S. census, Port Chester was the fifth-most populous village in New York State. In 2019, its population grew to a census-estimated 29,342 residents.
Located in southeast Westchester, Port Chester forms part of the New York City metropolitan statistical area and borders Connecticut and the town of Greenwich to the east. Port Chester is one of only 12 villages in New York still incorporated under a charter, while other villages are either incorporated or reincorporated under the provisions of Village Law.
The village is nicknamed the “Gateway to New England” and serves as a transportation hub between New England states and New York. Its economy is primarily stimulated by small businesses, the local government, and several national chain stores. Port Chester is a vivacious community with a rich history and a strong connection to the surrounding region.
Rochester
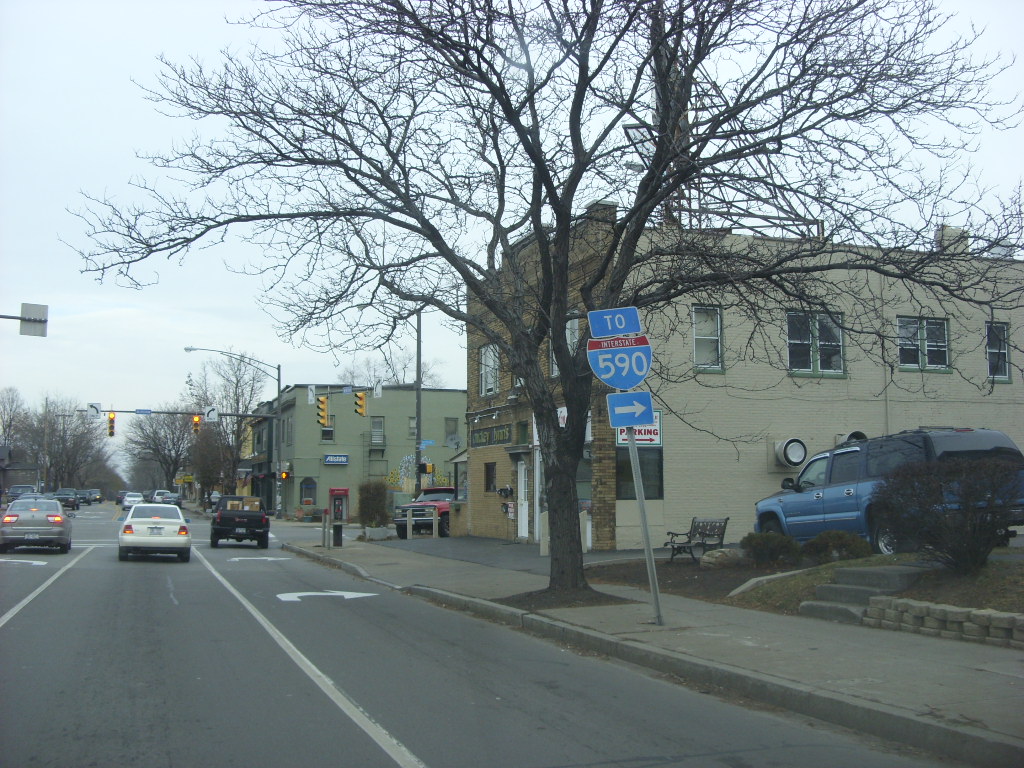

Rochester is a city located in the U.S. state of New York and serves as the seat of Monroe County. With a population of 211,328 as of the 2020 census, Rochester is the fourth-most populous city and 10th most-populated municipality in New York. The city forms the core of the larger Rochester metropolitan area in Western New York, with a population of over 1.09 million residents.
Rochester was one of the United States’ first boomtowns, initially due to the fertile Genesee River valley which gave rise to numerous flour mills, and then as a manufacturing center, which spurred further rapid population growth. The city has also played a key role in US history as a hub for social and political movements, particularly abolitionism and the women’s rights movement.
Rochester is the birthplace and home of several companies, including Eastman Kodak, Xerox, Bausch & Lomb, Wegmans, Gannett, Paychex, and Western Union, and the region has become a global center for science, technology, and research and development. Rochester is also known for its culture, including the Eastman School of Music and the Rochester International Jazz Festival, as well as several museums such as The Strong National Museum of Play and the George Eastman Museum.
Rochester is ranked highly in terms of livability and quality of life, due to its low cost of living, highly ranked public schools, and low unemployment rate. It is a global city, ranked by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network as having sufficiency status.
Rome
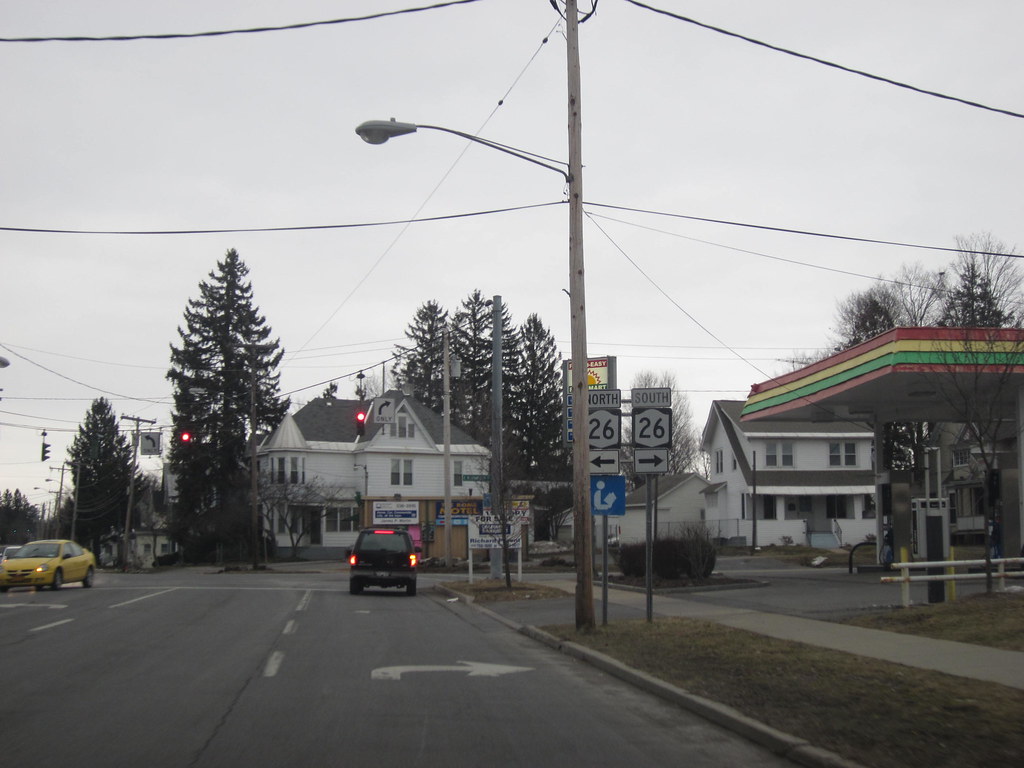

Rome is a city located in Oneida County, New York, in the central part of the state. With a population of 32,127 as of the 2020 census, Rome is one of two principal cities in the Utica-Rome Metropolitan Statistical Area, which lies in the “Leatherstocking Country” made famous by James Fenimore Cooper’s Leatherstocking Tales, set in frontier days before the American Revolutionary War.
The city developed at an ancient portage site of Native Americans, including the historic Iroquois nations, and this portage continued to be strategically important to Europeans, who used the main 18th and 19th-century waterways that connected New York City and the Atlantic seaboard to the Great Lakes.
Following the American Revolution, the settlement began to grow with the construction of the Rome Canal in 1796, which connected Wood Creek and the headwaters of the Mohawk River. The New York State Legislature converted the Town of Rome into a city on February 23, 1870, and Rome has since been known as the City of American History. The city has a rich history and is a popular destination for tourists interested in the region’s Native American and colonial heritage.
Auburn

Auburn is a city located in Cayuga County, New York, at the north end of Owasco Lake, one of the Finger Lakes in Central New York. With a population of 26,866 as of the 2020 census, Auburn is the largest city in Cayuga County and serves as the county seat.
The city is home to the maximum-security Auburn Correctional Facility, as well as several historic sites, including the William H. Seward House Museum and the home of abolitionist Harriet Tubman. The Seward House Museum is a National Historic Landmark, and the home of William H. Seward, who served as Secretary of State under Presidents Abraham Lincoln and Andrew Johnson.
Harriet Tubman’s home in Auburn was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1974 and is now a museum dedicated to her life and legacy as a conductor on the Underground Railroad. Auburn has a fascinating heritage and is a popular destination for tourists interested in the region’s abolitionist history.
Saratoga Springs

Saratoga Springs is a city located in Saratoga County, New York, with a population of 28,491 as of the 2020 census. The name Saratoga reflects the presence of mineral springs in the area, which has made it a popular resort destination for over 200 years. The city is home to the Saratoga Race Course, a thoroughbred horse racing track, and Saratoga Performing Arts Center, a music and dance venue.
The Saratoga Race Course is one of the oldest horse racing tracks in the United States and is known for hosting several major races, including the Travers Stakes and the Whitney Handicap. The Saratoga Performing Arts Center is a world-renowned venue that hosts a variety of performances, including ballet, opera, and popular music concerts.
Saratoga Springs is also known for its historic architecture, including the Saratoga Springs Preservation Foundation, which works to preserve and promote the city’s historic buildings.
The city’s official slogan is “Health, History, and Horses,” reflecting its reputation as a destination for health and wellness, its rich history, and its deep connection to the equestrian world. Saratoga Springs is a vibrant community with a unique blend of culture, history, and natural beauty, making it a great choice for visitors from around the world.
Schenectady

Schenectady is a city located in Schenectady County, New York, serving as the county seat. With a population of 67,047 as of the 2020 census, Schenectady is the ninth-most populous city in the state and the twenty-fifth most populous municipality by population. The city is situated in eastern New York, near the confluence of the Mohawk and Hudson rivers, and is part of the same metropolitan area as the state capital, Albany, which is about 15 miles southeast.
Schenectady was founded on the south side of the Mohawk River by Dutch colonists in the 17th century, many of whom came from the Albany area. The name “Schenectady” is derived from the Mohawk word skahnéhtati, meaning “beyond the pines,” and was used for the area around Albany, New York.
Schenectady developed rapidly in the 19th century as part of the Mohawk Valley trade, manufacturing, and transportation corridor, connected to the west by the Mohawk River and Erie Canal.
The city was home to nationally influential companies and industries such as General Electric and American Locomotive Company, which were powers into the mid-20th century. Schenectady was also part of emerging technologies, with GE collaborating in the production of nuclear-powered submarines and, in the 21st century, working on other forms of renewable energy.
Syracuse

Syracuse is a city and the county seat of Onondaga County, New York, with a population of 148,620 as of the 2020 census, making it the fifth-most populated city and the 13th-most populated municipality in the state of New York. The city is the economic and educational hub of Central New York, a region with over one million inhabitants.
Syracuse is also well-provided with convention sites, with a downtown convention complex. The city was named after the classical Greek city Syracuse, located on the eastern coast of the Italian island of Sicily. Historically, Syracuse has functioned as a major crossroad over the last two centuries, first between the Erie Canal and its branch canals, then of the railway network.
Today, Syracuse is at the intersection of Interstates 81 and 90, and its airport is the largest in the Central New York region. Syracuse is home to several prestigious institutions of higher education, including Syracuse University, SUNY Upstate Medical University, SUNY ESF, and Le Moyne College.
Utica

Utica is a city located in the Mohawk Valley and the county seat of Oneida County, New York, with a population of 65,283 as of the 2020 U.S. Census, making it the tenth-most populous city in New York State. The city is situated on the Mohawk River at the foot of the Adirondack Mountains, approximately 95 miles west-northwest of Albany, 55 miles east of Syracuse, and 240 miles northwest of New York City.
Utica and the nearby city of Rome anchor the Utica–Rome Metropolitan Statistical Area comprising all of Oneida and Herkimer Counties. Utica was formerly a river settlement inhabited by the Mohawk Nation of the Iroquois Confederacy and attracted European-American settlers from New England during and after the American Revolution.
In the 19th century, immigrants strengthened its position as a layover city between Albany and Syracuse on the Erie and Chenango Canals and the New York Central Railroad. The city’s infrastructure contributed to its success as a manufacturing center and defined its role as a worldwide hub for the textile industry.
However, like other Rust Belt cities, Utica underwent an economic downturn throughout the mid-20th century, consisting of industrial decline due to offshoring and the closure of textile mills, population loss caused by the relocation of jobs and businesses to suburbs and to Syracuse, and poverty associated with socioeconomic stress and a depressed tax base.
Despite this, Utica’s low cost of living has made it a melting pot for refugees from war-torn countries around the world, encouraging growth for its colleges and universities, cultural institutions, and economy.
Watertown

Watertown is a city located in, and the county seat of, Jefferson County, New York, with a population of 24,685 as of the 2020 United States Census, making it the largest city in the North Country. The city is approximately 25 miles south of the Thousand Islands, along the Black River about 5 miles east of where it flows into Lake Ontario.
Watertown is bordered by the town of Watertown to the south, east, and west and is served by the Watertown International Airport and the Watertown Daily Times newspaper. The Public Square Historic District, built in 1805, is located in the middle of Watertown and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.
Watertown was designated as the county seat of Jefferson County when it was split off from Oneida County in 1805. The city was incorporated as a village in 1816 and became a city in 1869, booming as an industrial center for Upstate New York by the early 20th century.
However, during the mid-1960s, many younger residents and businesses moved to Chicago, leading to the demolition of many historic buildings and a decline in population. The city serves as the commercial and financial center for the North Country and is located 30 miles from the Canadian border, with shopping by Canadian visitors important to Watertown’s economy. Watertown, South Dakota, was named in the city’s honor.
White Plains

White Plains is a city located in Westchester County, New York, with a population of 59,599 as of the 2020 census, making it the 29th-largest municipality in the state of New York. White Plains is an inner suburb of New York City and serves as the county seat and commercial hub of Westchester County, a densely populated suburban county that is home to about one million people.
The city is located in south-central Westchester County, with its downtown (Mamaroneck Avenue) located 25 miles north of Midtown Manhattan. According to the city government, the daytime weekday population is estimated at 250,000, demonstrating the city’s importance as a commercial and business hub.
White Plains is home to a vibrant downtown area, with numerous shopping, dining, and entertainment options. The city is also known for its excellent schools, including the White Plains Public Schools and several private schools. White Plains is easily accessible by car and public transportation, with the Metro-North Railroad providing frequent service to Grand Central Terminal in Midtown Manhattan.
Yonkers
Yonkers is a city located in Westchester County, New York, and a suburb of New York City, with a population of 211,569 as of the 2020 United States Census, making it the 9th–most populous incorporated place in New York State. The city is developed along the Hudson River and is classified as an inner suburb of New York City, located directly to the north of the Bronx and approximately 2.4 miles north of Marble Hill, Manhattan, the northernmost point in Manhattan.
Yonkers’s downtown is centered on a plaza known as Getty Square, where the municipal government is located, and serves as a major retail hub for Yonkers and the northwest Bronx. Yonkers is home to several attractions, including access to the Hudson River, Tibbetts Brook Park, Untermyer Park, the Hudson River Museum, the Saw Mill River daylighting, the Science Barge, and Sherwood House.
Yonkers Raceway, a harness racing track, also offers legalized video slot machine gambling and is known as Empire City. Major shopping areas are located in Getty Square, on South Broadway, at the Cross County Shopping Center and Westchester’s Ridge Hill, and along Central Park Avenue. Yonkers is considered a City of Seven Hills, with its hills including Park, Nodine, Ridge, Cross, Locust, Glen, and Church Hills.
Interstates
Interstate 81

Interstate 81 (I-81) is a major north-south highway in New York that extends 183.60 miles (295.48 km) from the Pennsylvania state line southeast of Binghamton to the Canadian border at Wellesley Island northwest of Alexandria Bay. The freeway runs through Central New York, serving the cities of Binghamton, Syracuse, and Watertown, and passes through the Thousand Islands in its final miles.
I-81 closely parallels US Route 11 (US 11) south of Watertown, the main north-south highway in Central New York prior to the construction of I-81. The road continues into the province of Ontario as Highway 137, a short route leading north to the nearby Highway 401.
The portion of I-81 in New York was originally developed as the Penn-Can Highway, one of four expressways proposed by the state in 1953. It was added to the Interstate Highway System and designated I-81 in 1957 and constructed in sections over the course of the next decade.
Interstate 87
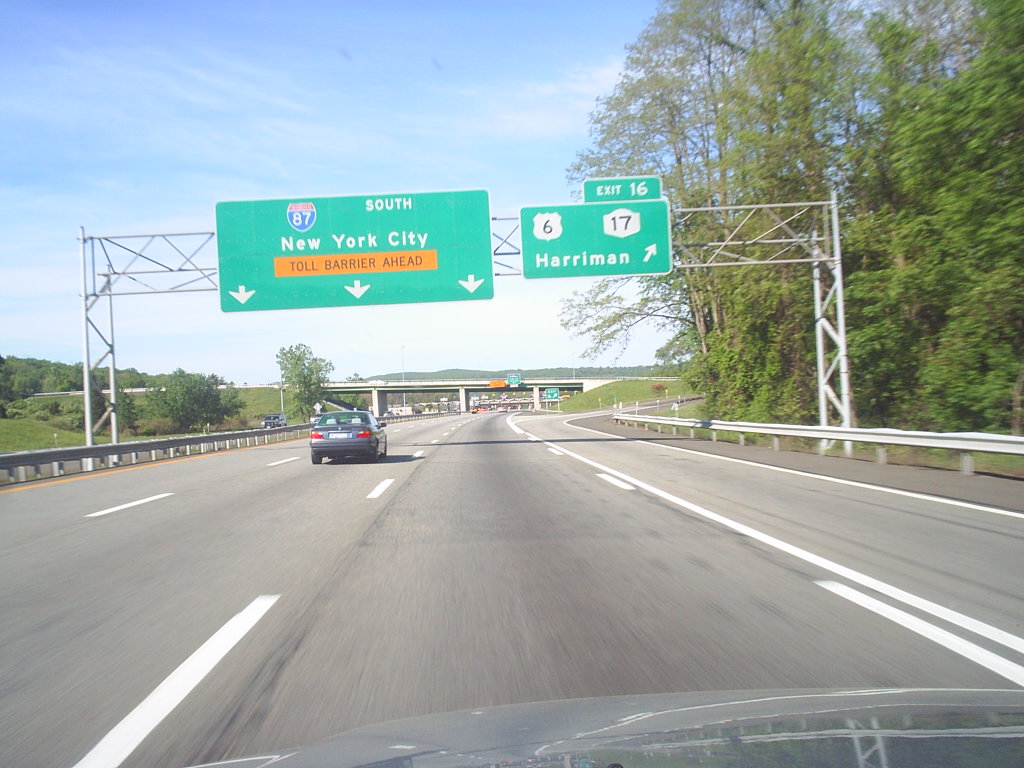

Interstate 87 (I-87) is a 333.49-mile-long (536.70 km) north-south Interstate Highway located entirely within the US state of New York. It is the main highway that connects New York City and Montreal, beginning at exit 47 off I-278 in the Bronx, just north of the Robert F. Kennedy Bridge and Grand Central Parkway.
The highway runs northward through the Hudson Valley, the Capital District, and the easternmost part of the North Country to the Canada-United States border in the town of Champlain, where it continues into Quebec as Autoroute 15 (A-15). I-87 connects with several regionally important roads, including I-95 in New York City, New York State Route 17 (NY 17; future I-86) near Harriman, I-84 near Newburgh, and I-90 in Albany.
The portion of I-87 south of Albany follows two controlled-access highways that predate the Interstate Highway designation, the Major Deegan Expressway (locally known as “the Deegan”) in New York City and the tolled New York State Thruway from the New York City line to Albany. North of Albany, I-87 follows the Adirondack Northway, a highway built in stages between 1957 and 1967.
Interstate 495
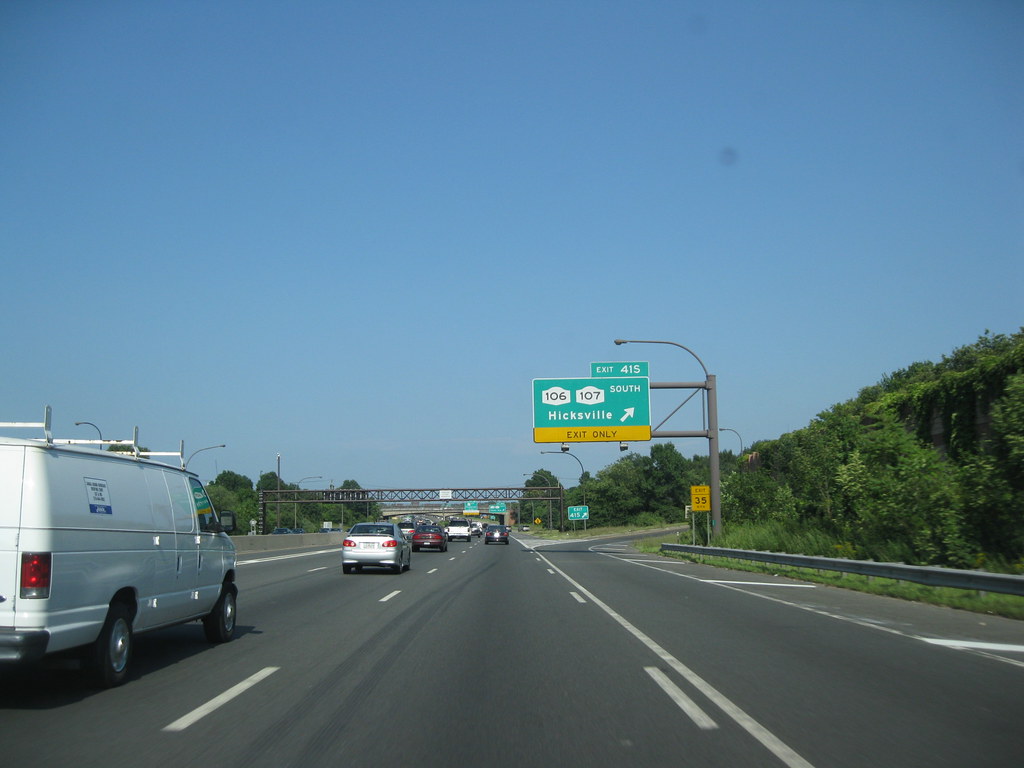

Interstate 495 (I-495), commonly known as the Long Island Expressway (LIE), is an auxiliary Interstate Highway in the US state of New York. It spans approximately 66 miles (106 km) along a west-east axis, traversing Long Island from the western portal of the Queens-Midtown Tunnel in Manhattan to County Route 58 (CR 58) in Riverhead in the east.
The highway is jointly maintained by the New York State Department of Transportation (NYSDOT), the New York City Department of Transportation (NYCDOT), MTA Bridges and Tunnels (TBTA), and the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey (PANYNJ). I-495 intersects with I-295 in Bayside, Queens, through which it connects with I-95.
The LIE designation technically refers to the stretch of highway in Nassau and Suffolk counties. The service roads that run parallel to either side of the expressway in Queens are signed as Borden Avenue and Queens Midtown Expressway and as Horace Harding Expressway and Horace Harding Boulevard.
Interstate 84

Interstate 84 (I-84) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that runs from Dunmore, Pennsylvania, to Sturbridge, Massachusetts, in the eastern United States. In New York, I-84 extends 71.46 miles (115.00 km) from the Pennsylvania state line at Port Jervis to the Connecticut state line east of Brewster.
As it heads east-west across the mid-Hudson Valley, it goes over two mountain ranges and crosses the Hudson River at the Newburgh-Beacon Bridge. It is the only limited-access road to cross New York from west to east between New York City and the Capital District, making it the main vehicular route between southern New England and Pennsylvania and points west.
The highway is maintained by the New York State Department of Transportation (NYSDOT), and the New York State Bridge Authority charges a toll for eastbound traffic crossing the Newburgh-Beacon Bridge. Construction of the highway began in 1960 and was completed 12 years later, becoming a major commercial artery and mainstay of the Hudson Valley economy.
Interstate 86

Interstate 86 (I-86) is an Interstate Highway that extends for 223.39 miles (359.51 km) through northwestern Pennsylvania and the Southern Tier region of New York. The highway has two segments, with the longer of the two beginning at an interchange with I-90 east of Erie, Pennsylvania, and ending just beyond the Chemung-Tioga county line at the Pennsylvania border.
The second segment extends from I-81 east of Binghamton to New York State Route 79 (NY 79) in Windsor. I-86 is part of Corridor T of the Appalachian Development Highway System and connects to US Route 219 (US 219) in Salamanca, I-390 near Avoca, and I-99/US 15 just west of Corning.
The highway was built in stages from the 1950s to the 1980s, and the I-86 designation was assigned in 1999 to the entirety of since-decommissioned Pennsylvania Route 17 (PA 17) and to the westernmost 177 miles (285 km) of NY 17. It has been extended eastward as more sections of the existing NY 17 freeway have been upgraded to Interstate Highway standards, with the current terminus at the Chemung-Tioga county line.
Interstate 88
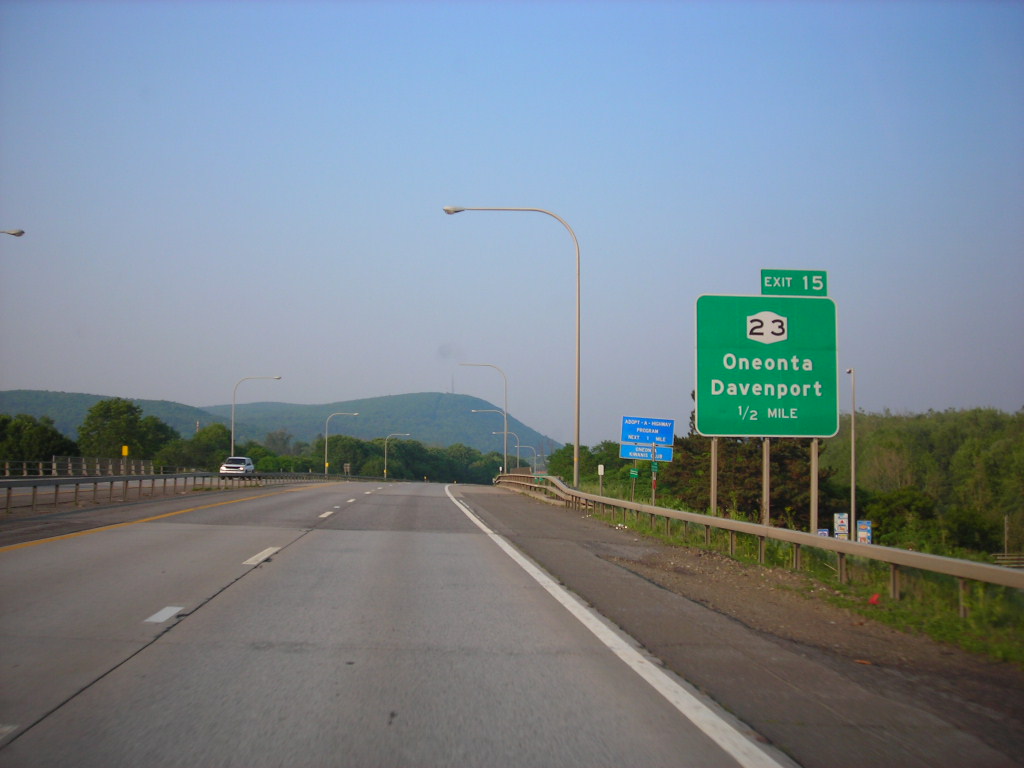

Interstate 88 (I-88) is an Interstate Highway located entirely within the US state of New York. It extends for 117.75 miles (189.50 km) in a northeast-southwest direction from an interchange with I-81 north of the city of Binghamton to an interchange with the New York State Thruway (I-90) west of Schenectady.
The freeway serves as an important connector route from the Capital District to Binghamton, Elmira (via New York State Route 17 or NY 17, I-86), and Scranton, Pennsylvania (via I-81). Although nominally signed as an east-west road as it has an even number, I-88 closely parallels NY 7, which was once the main route through the area. I-88 was assigned in 1968, and construction of the highway began soon afterward.
The first section of I-88 opened in the early 1970s, and the last piece of the freeway was finished in 1989. Early plans for I-88 called for the road to continue northeast to Troy, but the east end of the route was moved to Schenectady in the early 1980s.
Interstate 90

Interstate 90 (I-90) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that runs from Seattle, Washington, to Boston, Massachusetts. In the US state of New York, I-90 extends 385.48 miles (620.37 km) from the Pennsylvania state line at Ripley to the Massachusetts state line at Canaan, making it the second-longest highway in the state after New York State Route 17 (NY 17).
Most of the route is part of the tolled New York State Thruway, but two non-tolled sections exist along I-90. Within New York, I-90 has a complete set of auxiliary Interstates, which means that there are Interstates numbered I-190 through I-990 in the state, with no gaps in between.
For most of its length in New York, I-90 runs parallel to the former Erie Canal route, NY 5, US Route 20 (US 20), and the CSX Transportation railroad mainline that traverses the state. I-90 was assigned in 1957 as part of the establishment of the Interstate Highway System and was overlaid on the preexisting New York State Thruway from Pennsylvania to Albany. The Albany-Schodack freeway was completed in stages during the 1960s and 1970s and fully open by 1977.
Highways
Route 4

U.S. Route 4 (US 4) is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that runs from East Greenbush, New York, to Portsmouth, New Hampshire. In the US state of New York, US 4 extends 79.67 miles (128.22 km) from an intersection with US 9 and US 20 in East Greenbush to the Vermont state line northeast of Whitehall. While the remainder of US 4 east of New York is an east-west route, US 4 in New York is signed north-south due to the alignment the route takes through the state.
The route runs along the Hudson River from Troy to Hudson Falls and the Champlain Canal from Fort Ann to Whitehall, passing through several riverside and canalside communities. US 4 crosses several major east-west highways as it proceeds north, such as Interstate 90 (I-90) in East Greenbush, New York State Route 7 (NY 7) in Troy, NY 29 in Schuylerville, and NY 149 in Fort Ann.
It also overlaps with the north-south NY 22 for six miles (9.7 km) from Comstock to Whitehall and with NY 32 for a total of 16 miles (26 km) between Waterford and Bemis Heights and from Schuylerville to Northumberland. US 4 was assigned in 1926, initially extending from Glens Falls to the Vermont border near Whitehall by way of Hudson Falls, and was extended southward to its present terminus in East Greenbush as part of the 1930 renumbering of state highways in New York.
Route 6

U.S. Route 6 (US 6) in New York spans 77.85 miles (125.29 km) from the Pennsylvania state line at Port Jervis to the Connecticut state line east of Brewster. Near both ends, it runs in close proximity to Interstate 84 (I-84), which otherwise takes a more northerly route through Downstate New York. US 6 skirts the northern fringe of the New York metropolitan area and is not as important a transportation artery in New York as it is in some other states.
The route, except for a section concurrent with the expressway portion of New York State Route 17 (NY 17; the future I-86) and another brief, similar stretch in Peekskill, is a two-lane road in New York. Two stretches are shared with US 202. It goes through three of New York’s traffic circles, more than any other highway in the state, and is part of the only concurrency of three U.S. routes in the state.
The route passes through some of the region’s more memorable scenery, particularly the Hudson Highlands in the form of Harriman and Bear Mountain state parks. It crosses the Hudson River at the historic Bear Mountain Bridge, and other highlights include the Shawangunk Ridge in the west and New York City’s reservoirs in the east.
Route 9

U.S. Route 9 (US 9) is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that runs from Laurel, Delaware, to Champlain, New York. In New York, US 9 extends 324.72 miles (522.59 km) from the George Washington Bridge in Manhattan to an interchange with Interstate 87 (I-87) just south of the Canadian border in the town of Champlain, making it the longest north-south U.S. Highway in New York.
The section of US 9 in New York passes through busy urban neighborhoods, suburban strips, and forested wilderness. It is known as Broadway in Upper Manhattan, the Bronx, and much of Westchester County, and passes through the downtown of Albany, the state capital, as well as Saratoga Springs.
US 9 penetrates into the deep recesses of the Adirondack Park and runs along the shore of Lake Champlain, where it is part of the All-American Road known as the Lakes to Locks Passage. US 9 spawns more letter-suffixed state highways than any other route in New York, including the longest, 143-mile (230 km) New York State Route 9N (NY 9N). For much of its southern half, it follows the Hudson River closely, and in the north, it tracks I-87 (Adirondack Northway).
Route 9W

U.S. Route 9W (US 9W) is a north-south United States Numbered Highway that begins in Fort Lee, New Jersey, as Fletcher Avenue crosses the US 1/9, US 46, and Interstate 95 (I-95) approaches to the George Washington Bridge, and heads north up the west side of the Hudson River to US 9 in Albany, New York. US 9W is a westerly alternate route of US 9 between the two locations.
The route directly serves three cities – Newburgh, Kingston, and Albany – and enters the vicinity of several others. As the route heads north, it connects to several highways of regional importance, including I-84, US 209, New York State Route 23 (NY 23), and US 20. Much of US 9W parallels the New York State Thruway and NY 32; additionally, the latter overlaps with US 9W in four different locations.
Route 11

U.S. Route 11 (US 11) is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that runs from New Orleans, Louisiana, to the Canada-United States border at Rouses Point, New York. In the state of New York, US 11 extends for 318.66 miles (512.83 km) from the Pennsylvania state line south of the Southern Tier city of Binghamton to the Canada-United States border at the North Country village of Rouses Point, where it becomes Route 223 upon entering Quebec.
The portion of US 11 south of Watertown follows a mostly north-south alignment and is paralleled by Interstate 81 (I-81) while the part of the route north of Watertown follows a more east-west routing, parallel to but not directly on the St. Lawrence River. The portion of US 11 in New York passes through the central district of four cities: Binghamton, Cortland, Syracuse, and Watertown.
East of Watertown, the route traverses mostly rural terrain and serves only small villages, such as Potsdam, Malone, and Champlain. While the portion of US 11 between the Pennsylvania state line and Watertown is merely an alternate route to I-81, the section east of Watertown is the primary long-distance route across the North Country of New York. US 11 was designated as part of the 1926 establishment of the U.S. Numbered Highway System and was first signed in New York in 1927, replacing New York State Route 2 (NY 2). One of US 11’s three suffixed routes, NY 11C, follows a former routing of US 11.
Route 20

U.S. Route 20 (US 20) is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that runs from Newport, Oregon, to Boston, Massachusetts. In the U.S. state of New York, US 20 extends 372.32 miles (599.19 km) from the Pennsylvania state line at Ripley to the Massachusetts state line in the Berkshires, making it the longest surface road in New York.
US 20 runs near the Lake Erie shore from Ripley to Buffalo and passes through the southern suburbs of Buffalo, the Finger Lakes, the glacial moraines of Central New York, and the city of Albany before crossing into Massachusetts. Although it bypasses major cities like Syracuse and Utica, it is a major artery in many of the outlying areas it passes through in the hilly fringes of the Allegheny Plateau, often expanding to four lanes with extensive commercial strip development.
From Oneida County to Albany, the road follows the historic Cherry Valley Turnpike, built at the beginning of the 19th century to connect Albany and several important villages. US 20 was assigned in 1926 and was the state’s main east-west route from that time until the Thruway was completed in the 1950s.
Route 20A

U.S. Route 20A (US 20A) is an east-west alternate route of US 20 that extends for 83.59 miles (134.53 km) across the western portion of New York in the United States. It leaves US 20 in Hamburg, a suburb of Buffalo, and rejoins it in East Bloomfield about five miles west of Canandaigua, the county seat of Ontario County.
Most of the route is known as Big Tree Road; outside Highmark Stadium, the highway is known as the Timothy J. Russert Highway in memory of Buffalo native Tim Russert. While the main line of US 20 takes a direct path between Hamburg, Buffalo, and East Bloomfield via Avon, US 20A veers to the south to serve several villages and hamlets, including the villages of Geneseo and Warsaw.
As the route heads east, US 20A connects to several north-south freeways, such as NY 400 outside of East Aurora and Interstate 390 (I-390) between Geneseo and Lakeville. Outside of the communities that dot the highway, US 20A is a two-lane, rural highway. US 20A was assigned to US 20’s former routing west of Lakeville and all of NY 254 in 1939.
Route 44

US 44 begins at an intersection with US 209 and NY 55 west of the hamlet of Kerhonkson in the town of Wawarsing in Ulster County. NY 55, concurrent with US 209 southwest of this point, turns east onto US 44, forming an overlap as the two routes proceed eastward across Ulster County.
Midway between Kerhonkson and Gardiner and just north of NY 299, US 44 and NY 55 traverse a hairpin turn made necessary by the surrounding Shawangunk Ridge. US 44 continues eastward through the town of Pleasant Valley in Dutchess County, where it intersects with the Taconic State Parkway.
The route then turns southeastward, passing through the town of Washington before entering the town of North East in Columbia County. US 44 then crosses the state line into Connecticut, where it continues eastward towards Hartford. The road was originally designated in 1926 as part of the U.S. Numbered Highway System and has since undergone several realignments and modifications.
Route 62

U.S. Route 62 (US 62) is a part of the U.S. Highway System that travels from the United States–Mexico border at El Paso, Texas, to Niagara Falls, New York. In the U.S. state of New York, US 62 extends 102.77 miles (165.39 km) from the New York–Pennsylvania border south of Jamestown to an intersection with New York State Route 104 (NY 104) in downtown Niagara Falls.
It is the only north-south mainline U.S. highway in Western New York, bypassing the city of Jamestown and serving the cities of Buffalo and Niagara Falls, along with several villages. US 62 was extended into New York in 1932 and originally was concurrent with the state highways that had previously been designated along its routing, including NY 18, NY 60, NY 83, and NY 241.
These concurrencies were eliminated individually during the 1940s and 1960s, with the last of the four concurrencies, NY 18 from Dayton to Niagara Falls, being removed in 1962. US 62 has one special route, US 62 Business, located in Niagara Falls. US 62 Business is a former routing of US 62 within the city and was once NY 62A.
Route 209

US 6 and US 209 remain concurrent as they enter Port Jervis, but after less than a mile, US 209 strikes out to the northeast again on its own. After leaving the city, it enters the valley between the Shawangunk Ridge and the Catskill Plateau to its west, following the Neversink River until crossing it just prior to the hamlet of Cuddebackville. The scenery is rural and the settlements along the road are few, with only one blinker between Port Jervis and the Sullivan County line.
The road follows along some of the old Delaware and Hudson Canal, a National Historic Landmark, and passes Wurtsboro Airport, out of the county into Ulster County, and eventually reaches another village, more bustling Ellenville. At another small hamlet, Kerhonkson, NY 55 leaves to join US 44 at the latter’s western terminus. The valley begins to widen as another road, NY 213, joins for a mile before leaving at a blinker in downtown Stone Ridge.
To the north, the road eventually widens into four lanes, then four divided lanes as the freeway begins just short of NY 28 just west of Kingston. US 209 crosses the New York State Thruway (I-87) but does not have an exit. The eastbound highway remains an expressway to the Kingston–Rhinecliff Bridge. US 209, however, does not make it that far, becoming NY 199 where it crosses over US 9W.
Route 219

U.S. Route 219 (US 219) is a part of the U.S. Highway System that runs from Rich Creek, Virginia, to West Seneca, New York. In the U.S. state of New York, US 219 extends 67.63 miles (108.84 km) from the Pennsylvania state line at Carrollton to an interchange with the New York State Thruway (Interstate 90 or I-90) at exit 55 in West Seneca, southeast of downtown Buffalo.
The path of US 219 in New York mostly follows that of New York State Route 62, which was assigned in the 1930 renumbering of state highways in New York and extended from Great Valley north to Buffalo via Ellicottville, the hamlet of Ashford, Springville, and Hamburg. From Ellicottville to Springville, NY 62 utilized modern NY 242 and NY 240.
It was renumbered to NY 75 in 1932 and became part of US 219 from Hamburg south when the U.S. Highway was extended into New York in 1935. In Cattaraugus County, the area surrounding US 219 is predominantly rural. However, in northern Cattaraugus County, US 219 becomes an expressway leading through Erie County and into the heart of Buffalo.
The route serves the villages of Ellicottville and Springville, where it meets New York State Route 242 (NY 242) and NY 39, respectively, and indirectly serves Hamburg via NY 391. Long-term plans for the expressway call for it to extend from West Seneca south to Salamanca.

