Virginia, located in the southeastern region of the United States, is a state known for its rich history, stunning natural beauty, and vibrant culture. With its picturesque beaches, charming small towns, and bustling urban centers, Virginia offers a unique blend of nature and culture. To help visitors and residents navigate this beautiful state, we have created a detailed map of Virginia with cities and highways.
This map highlights Virginia’s major cities, including Richmond, Virginia Beach, Norfolk, and Roanoke, as well as its primary highways and roads. Whether you’re planning a road trip or simply want to explore Virginia’s unique landscape and culture, this map is an essential tool. So, grab your map and get ready to discover all that Virginia has to offer, from its world-renowned historic landmarks to its stunning national parks and everything in between.
Printable Virginia Map With Cities and Highways
Cities
Alexandria
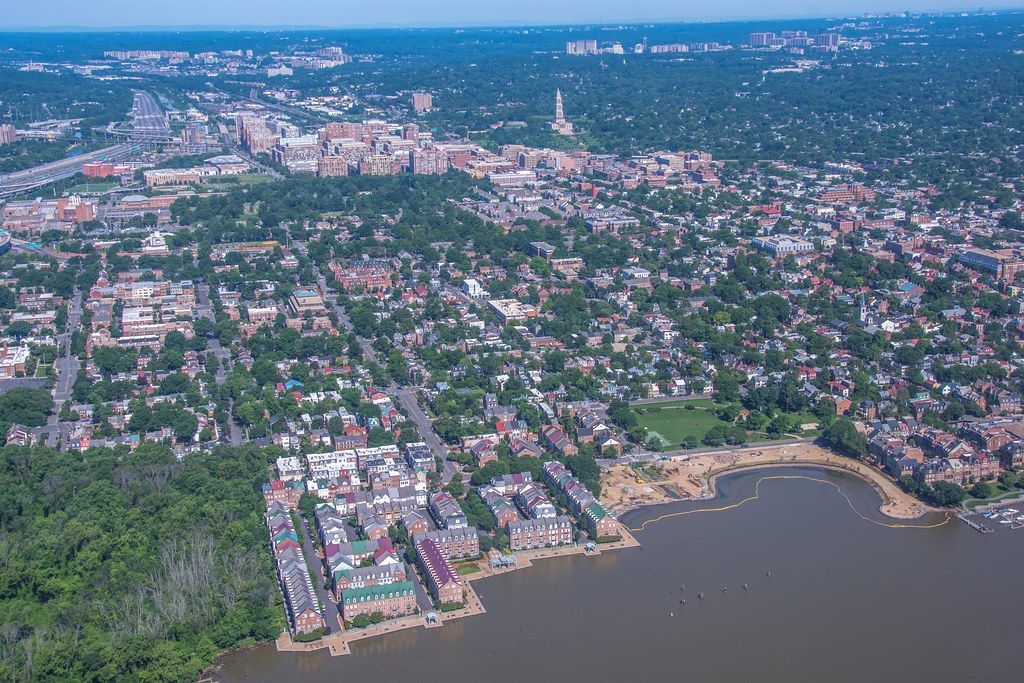

Alexandria is a vibrant and historic independent city located in the northern region of the Commonwealth of Virginia, United States. The city lies on the western bank of the Potomac River, approximately 7 miles south of downtown Washington, D.C. With a population of 159,467 in 2020, Alexandria is the 6th most populous city in Virginia and the 169th most populous city in the nation.
The city is largely populated by professionals working in the federal civil service, in the U.S. military, or for one of the many private companies that contract to provide services to the federal government. The historic center of Alexandria, known as Old Town Alexandria, is a major draw for both residents and visitors, with its concentration of boutiques, restaurants, antique shops, and theaters.
The city is also home to several large employers, including the U.S. Department of Defense and the Institute for Defense Analyses. With its rich history, vibrant culture, and proximity to the nation’s capital, Alexandria is a unique and exciting place to live, work, and visit.
Annandale
Annandale is a census-designated place (CDP) located in Fairfax County, Virginia. With a population of 43,363 as of the 2020 United States Census, Annandale is a vibrant community that is home to the oldest and largest branch of the Northern Virginia Community College system.
Annandale is also known for its thriving Koreatown, which is one of the largest in the Washington, D.C. area. The community is home to a diverse population, with a mix of residential, commercial, and industrial areas.
Residents enjoy easy access to nearby parks and recreational areas, as well as a variety of shopping and dining options. With its convenient location and strong sense of community, Annandale is a great place to call home for both families and professionals.
Arlington County

Arlington County is a bustling and diverse county located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River, directly across from Washington, D.C. The county is coextensive with the U.S. Census Bureau’s census-designated place of Arlington and is the second-largest city in the Washington metropolitan area, although it does not have the legal designation of an independent city or incorporated town under Virginia state law.
With a population of 238,643 in 2020, Arlington County is the sixth-largest county in Virginia by population and the largest unincorporated community in the United States. If Arlington County were incorporated as a city, it would be the third-most populous city in Virginia. The county is home to several major landmarks, including The Pentagon, which is the headquarters of the U.S. Department of Defense, Reagan National Airport, and Arlington National Cemetery.
Arlington is also a hub for higher education, with several universities and graduate programs located in the county. Additionally, Arlington is home to the co-headquarters of Amazon and the global headquarters of many aerospace manufacturing and defense industry companies. With its dynamic economy and rich cultural offerings, Arlington is an energetic and exciting place to live, work, and visit.
Blacksburg

Blacksburg is a charming and vibrant incorporated town located in Montgomery County, Virginia, United States. With a population of 44,826 at the 2020 census, Blacksburg is a thriving community that is dominated economically and demographically by the presence of Virginia Tech.
The town, along with Christiansburg and the city of Radford, make up the Blacksburg-Christiansburg Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses those jurisdictions and all of Montgomery, Pulaski, and Giles counties for statistical purposes. The MSA has an estimated population of 181,863 and is currently one of the fastest-growing MSAs in Virginia.
Blacksburg is also home to Blacksburg High School, which is often ranked among the top schools in the nation for its academics. The school’s soccer, track, and cross-country teams are also among the top in the state. With its strong sense of community, beautiful natural surroundings, and top-notch educational opportunities, Blacksburg is a great place to call home for both families and professionals.
Bristol

Bristol is a charming independent city located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 17,219. The city is unique in that it is the twin city of Bristol, Tennessee, with the state line running down the middle of its main street, State Street.
Bristol, Virginia is surrounded on three sides by Washington County, Virginia, which is combined with the city for statistical purposes. It is a principal city in the Kingsport-Bristol metropolitan area, which had a population of 307,614 in 2020. The metro area is a component of the larger Tri-Cities region of Tennessee and Virginia, with a population of 508,260 in 2020.
Bristol offers a delightful downtown area with a variety of shops, restaurants, and cultural attractions. With its distinctive location and robust sense of community, Bristol is a great place to call home.
Chesapeake
Chesapeake is a thriving independent city located in Virginia, United States. With a population of 249,422 at the 2020 census, Chesapeake is the second-most populous city in Virginia and the tenth largest in the Mid-Atlantic. The city is included in the Hampton Roads metropolitan area and was organized in 1963 by voter referendums approving the political consolidation of the city of South Norfolk with the remnants of the former Norfolk County, which dated to 1691.
Chesapeake is the second-largest city by land area in the Commonwealth of Virginia and the 17th-largest in the United States. The city is a diverse mix of urban areas, protected farmland, forests, and wetlands, including a substantial portion of the Great Dismal Swamp National Wildlife Refuge.
Chesapeake’s location on the Atlantic Intracoastal Waterway provides miles of waterfront industrial, commercial, and residential property. The city is also home to the international headquarters of Dollar Tree. With its combination of natural beauty and economic opportunity, Chesapeake is a brilliant area in which to settle down.
Colonial Heights
Colonial Heights is a marvelous independent city located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 18,170. The Bureau of Economic Analysis combines the City of Colonial Heights (along with the City of Petersburg) with Dinwiddie County for statistical purposes.
The city is located in the Tri-Cities area of the Richmond Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA), which is a region that includes the cities of Richmond, Petersburg, and Hopewell, as well as the counties of Chesterfield, Hanover, Henrico, and New Kent. Colonial Heights offers a quaint downtown area with a variety of shops, restaurants, and cultural attractions.
The city is also home to several parks and recreational areas, providing residents with ample opportunities for outdoor activities. With its pleasing location and a welcoming sense of community, Colonial Heights is a great place to live or to work.
Dale City
Dale City is a vibrant census-designated place (CDP) located in Prince William County, Virginia, United States. The community is situated 25 miles (40 km) southwest of Washington, D.C., and is an annex of Woodbridge, Virginia. As of 2020, the total population was 72,088.
Dale City is roughly bounded by Hoadly Road to the northwest, Prince William Parkway to the north, Smoketown Road to the northeast, Gideon Drive to the east, and Cardinal Drive to the south. The community offers a mix of residential, commercial, and industrial areas, providing residents with a variety of shopping and dining options.
Dale City is also home to several parks and recreational areas, including the Prince William Forest Park, which offers hiking, camping, and other outdoor activities. With its convenient setting and a pleasant sense of community, Dale City is a wonderful destination in the locality.
Danville
Danville is a historic independent city located in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. The city is situated in the Southside Virginia region and on the fall line of the Dan River. Danville was a center of tobacco production and was an area of Confederate activity during the American Civil War, due to its strategic location on the Richmond and Danville Railroad.
In April 1865, it briefly served as the final capital of the Confederate States before its surrender later that year. Today, Danville is the principal city of the Danville, Virginia Micropolitan Statistical Area, with a population of 42,590 as of the 2020 census. The city is bounded by Pittsylvania County and Caswell County, North Carolina to the south and hosts the Danville Otterbots baseball club of the Appalachian League.
Danville has a rich and complex history, including a period during the Reconstruction era when it had an African-American majority and African-American political representatives of the Readjuster Party until after the Danville Massacre and Democrats regaining control locally and statewide. The area also saw violence during the civil rights era.
Fredericksburg
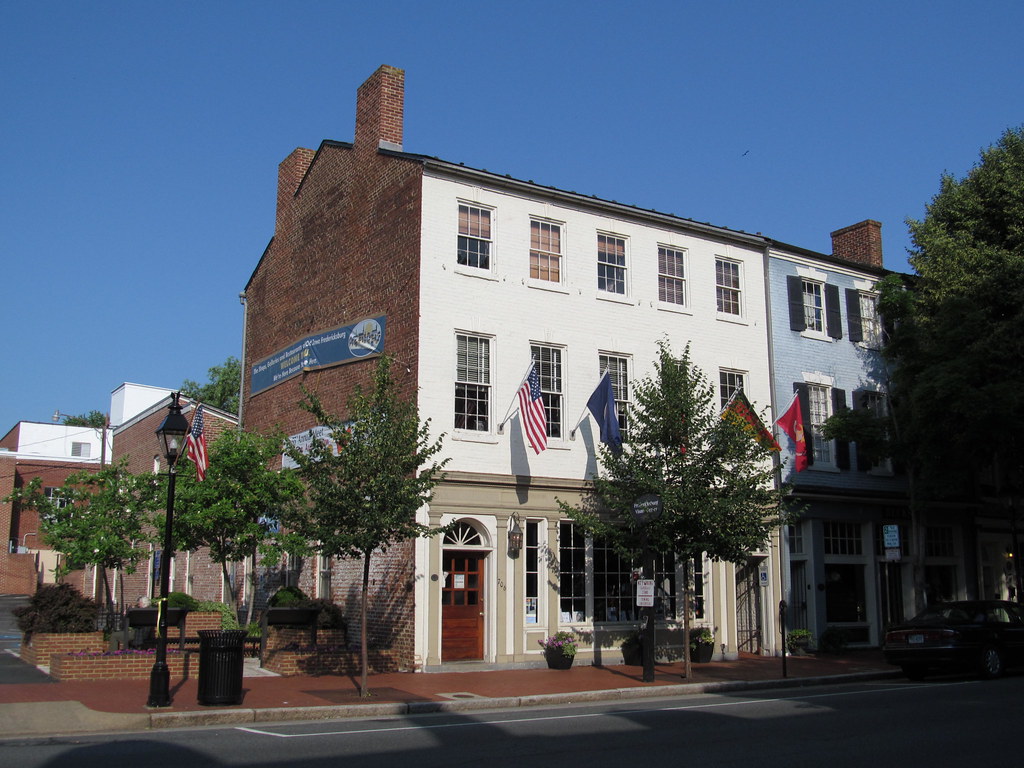

Fredericksburg is a delightful independent city located in Virginia, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 27,982. The city is situated 48 miles (77 km) south of Washington, D.C., and 53 miles (85 km) north of Richmond. The Bureau of Economic Analysis of the United States Department of Commerce combines the city of Fredericksburg with neighboring Spotsylvania County for statistical purposes.
Fredericksburg is located near where the Rappahannock River crosses the Atlantic Seaboard fall line and was a prominent port in Virginia during the colonial era. The city played a significant role in the Civil War, as it was located halfway between the capitals of the opposing forces and was the site of the Battle of Fredericksburg and the Second Battle of Fredericksburg.
Today, these battles are preserved, in part, as the Fredericksburg and Spotsylvania National Military Park. Fredericksburg is also home to Central Park, the second-largest mall on the East Coast, and the Spotsylvania Towne Centre, located in Spotsylvania County, adjacent to the city.
Major employers in Fredericksburg include the University of Mary Washington, Mary Washington Healthcare, and GEICO. With its rich history, beautiful natural landscapes, and flourishing economy, Fredericksburg is a marvelous place to settle.
Front Royal

Front Royal is a charming town located in Warren County, Virginia, United States. As the only incorporated town in the county, it serves as the county seat of Warren County. The population was 15,011 at the 2020 census, making it a small but energetic community.
Front Royal is known for its beautiful natural surroundings, including the nearby Shenandoah National Park and the Appalachian Trail. The town offers a variety of outdoor recreational activities, including hiking, fishing, and camping.
Front Royal also has a fascinating heritage, with many historic buildings and landmarks, including the Warren Rifles Confederate Museum and the Belle Boyd Cottage. With its small-town charm, natural beauty, and sense of history, Front Royal is a satisfying place to call home for those looking for a peaceful and relaxing lifestyle.
Hampton

Hampton is a dynamic independent city located in Virginia, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 137,148, making it the 7th-most populous city in Virginia and the 204th-most populous city in the nation. Hampton is a part of the Hampton Roads metropolitan area, the 37th-largest in the United States, with a total population of 1,799,674 in 2020.
The area is known as “America’s First Region” and includes the independent cities of Chesapeake, Virginia Beach, Newport News, Norfolk, Portsmouth, and Suffolk, as well as other smaller cities, counties, and towns of Hampton Roads. Hampton has a rich history, tracing its roots to Old Point Comfort, the home of Fort Monroe for almost 400 years.
Since consolidation in 1952, Hampton has included the former Elizabeth City County and the incorporated town of Phoebus. The city is also home to historic Hampton University, which was established after the end of the American Civil War to provide education for newly freed former slaves and area Native Americans.
In the 20th century, Hampton became the location of Langley Air Force Base, NASA Langley Research Center, and the Virginia Air and Space Center. The city features many miles of waterfront and beaches, as well as a wide array of business and industrial enterprises, retail and residential areas, historical sites, and other points of interest, such as a NASCAR short track, the oldest Anglican parish in the Americas (1610), and a moated, six-sided, historical bastion fort.
Harrisonburg
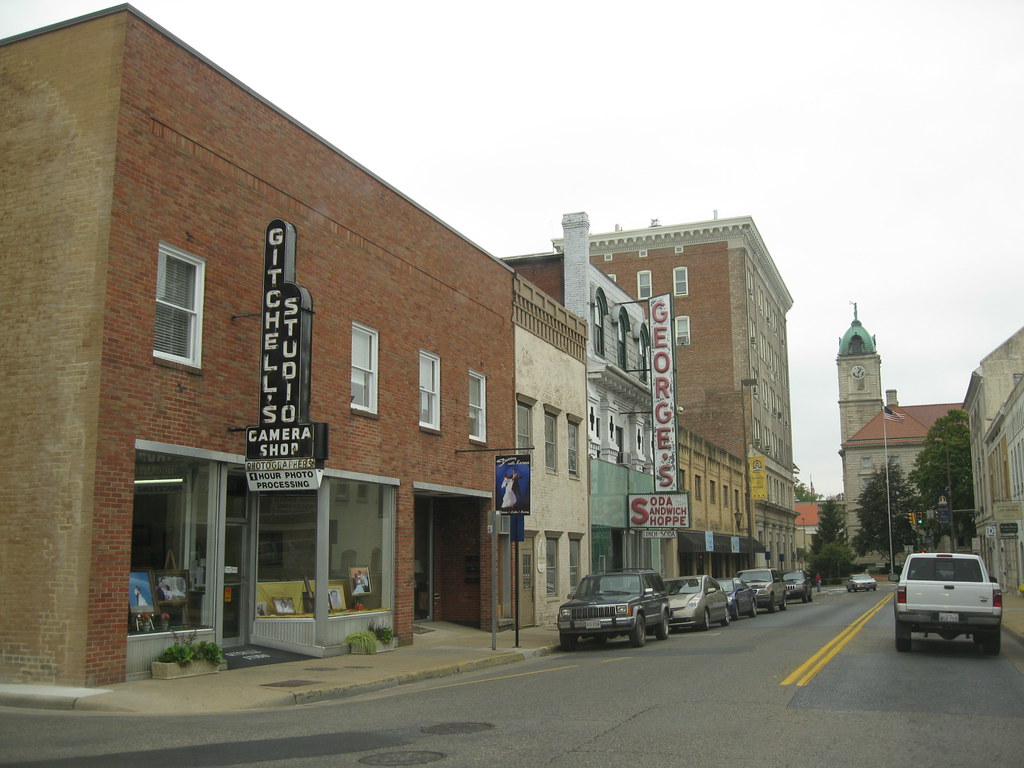

Harrisonburg is a vibrant independent city located in the Shenandoah Valley region of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. It also serves as the county seat of the surrounding Rockingham County, although the two are separate jurisdictions. At the 2020 census, the population was 51,814.
The city is home to James Madison University (JMU), a public research university with an enrollment of over 20,000 students, and Eastern Mennonite University (EMU), a private, Mennonite-affiliated liberal arts university. Although the city has no historical association with President James Madison, JMU was named in his honor as Madison College in 1938 and renamed as James Madison University in 1977.
EMU largely owes its existence to the sizable Mennonite population in the Shenandoah Valley. Harrisonburg is also a bastion of ethnic and linguistic diversity, with over 1,900 refugees settled in the city since 2002. As of 2014, Hispanics or Latinos of any race make up 19% of the city’s population, and Harrisonburg City Public Schools (HCPS) students speak 55 languages in addition to English, with Spanish, Arabic, and Kurdish being the most common languages spoken.
Over one-third of HCPS students are English as a second language (ESL) learners. Language learning software company Rosetta Stone was founded in Harrisonburg in 1992, and the multilingual “Welcome Your Neighbors” yard sign originated in Harrisonburg in 2016.
Laurel

Laurel is a charming census-designated place (CDP) located in western Henrico County, Virginia. The population was 16,713 at the 2010 United States Census, and it serves as the county seat of Henrico County. Laurel is home to the Laurel Skate Park, which recently underwent renovations to make it safer for visitors.
The bowl was filled in with smooth concrete, and the vertical ramp was removed to make way for new amenities. The park is a popular destination for skateboarders and BMX riders in the area. Laurel is also the location of the Laurel Industrial School Historic District, a site that played an important role in the education of African-American children during the segregation era.
The district is listed on the National Register of Historic Places and serves as a reminder of the struggles and triumphs of the African-American community in Virginia. With its intriguing history and vibrant community spirit, Laurel is a rewarding place to visit and call home.
Leesburg

Leesburg is a historic town located in and serving as the county seat of Loudoun County, Virginia, United States. Settlement in the area began around 1740 and is named for the Lee family, early leaders of the town. Located 33 miles (53 km) west-northwest of Washington, D.C., Leesburg is situated along the base of Catoctin Mountain and close to the Potomac River.
The town is the northwestern terminus of the Dulles Greenway, a private toll road that connects to the Dulles Toll Road at Washington Dulles International Airport. Its population was 48,250 as of the 2020 Census and is estimated to be 48,908 in 2021. Leesburg has undergone considerable growth and development over the last 30 years, transforming from a small, rural, Piedmont town to a suburban bedroom community for commuters to the national capital.
The town is home to professional soccer team Loudoun United FC of the USL Championship division, who play their home matches at Segra Field, a soccer-specific stadium located within Phillip A. Bolen Park, and adjacent to Loudoun Soccer Park. The Federal Aviation Administration’s Washington Air Route Traffic Control Center is also located in Leesburg.
Lynchburg
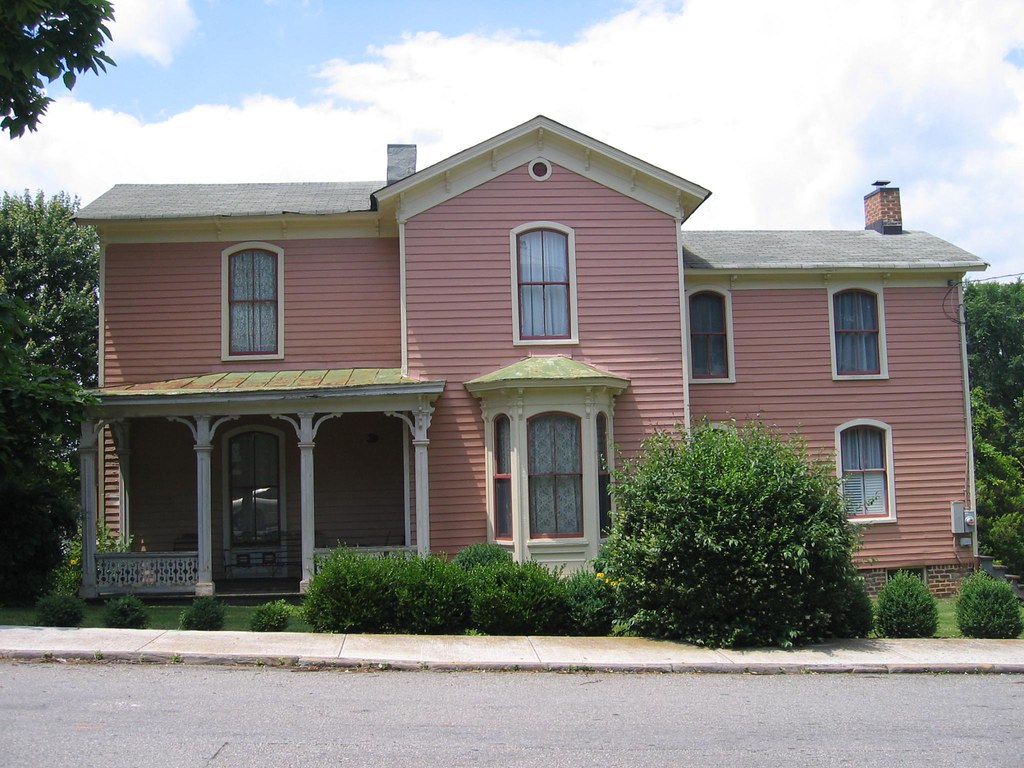

Lynchburg is a bustling independent city located in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. First settled in 1757 by ferry owner John Lynch, the city’s population was 79,009 at the 2020 census, making Lynchburg the 11th most populous city in Virginia. Located in the foothills of the Blue Ridge Mountains along the banks of the James River, Lynchburg is known as the “City of Seven Hills” or the “Hill City”.
In the 1860s, Lynchburg was the only city in Virginia that was not recaptured by the Union before the end of the American Civil War. Lynchburg lies at the center of a wider metropolitan area close to the geographic center of Virginia. It is the fifth-largest MSA in Virginia, with a population of 261,593.
The city is also home to several institutions of higher education, including Virginia University of Lynchburg, Randolph College, University of Lynchburg, Central Virginia Community College, and Liberty University. Nearby cities include Roanoke, Charlottesville, and Danville. With its interesting heritage and picturesque location, Lynchburg is a satisfying area for tourists and residents.
Manassas
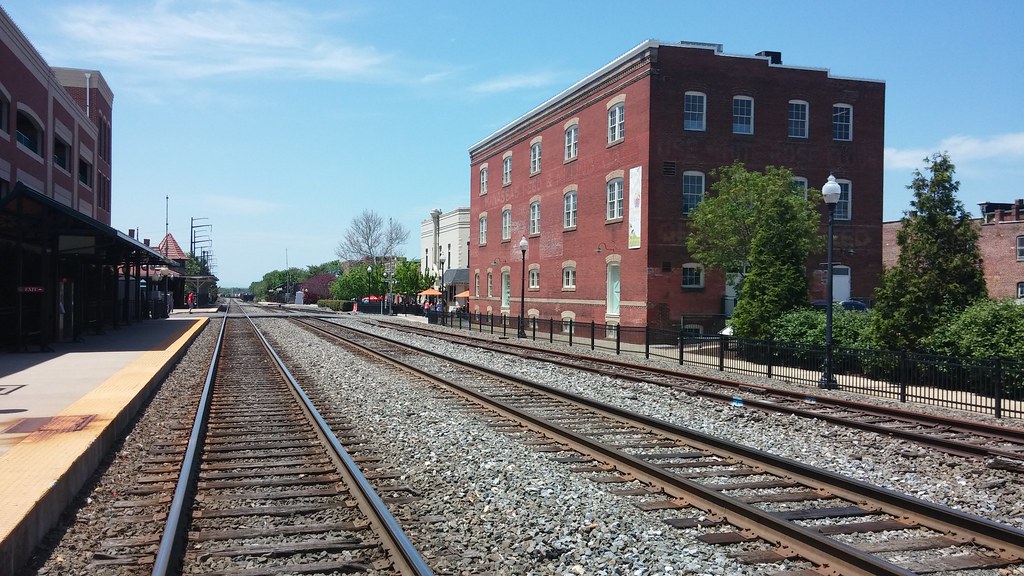

Manassas, formerly known as Manassas Junction, is a lovely independent city located in the Commonwealth of Virginia, United States. The population was 42,772 at the 2020 Census. Manassas serves as the county seat of Prince William County, although the two are separate jurisdictions.
The city also borders the independent city of Manassas Park, Virginia. The Bureau of Economic Analysis includes both Manassas and Manassas Park with Prince William County for statistical purposes.
Manassas is home to several historic sites dating from 1850 to 1870, including the 38-acre (15-hectare) county courthouse, which is located on county property. The city is part of the Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV Metropolitan Statistical Area and is in the Northern Virginia region.
Martinsville

Martinsville is a charming independent city located in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 13,485. A community of both Southside and Southwest Virginia, Martinsville serves as the county seat of Henry County, although the two are separate jurisdictions.
The Bureau of Economic Analysis combines the city of Martinsville with Henry County for statistical purposes. Martinsville is the principal city of the Martinsville Micropolitan Statistical Area, with a population of 63,765 as of the 2020 census.
The city is also home to the iconic Martinsville Speedway, which is shaped like a paper clip and is the shortest track in the NASCAR Cup Series at 0.526 miles (847 m). The speedway is located just outside the city near the town of Ridgeway and is one of the first paved “speedways.”
Mount Vernon

Mount Vernon is a scenic census-designated place (CDP) and unincorporated community located in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. The population was 12,416 at the 2010 census. The area is primarily known for its historical significance and natural beauty, attracting over one million tourists each year.
The name “Mount Vernon” is drawn from the Mount Vernon estate, the home of George Washington located south of Alexandria. While the name is often used locally to refer to the entire unincorporated area between Old Town Alexandria and Fort Belvoir, Mount Vernon as defined by the Census Bureau encompasses only the portion bounded by the Potomac River to the south, Fort Belvoir to the west, U.S. Route 1 to the north, and Little Hunting Creek to the east.
With its rich history and stunning natural surroundings, Mount Vernon is a popular destination for visitors and residents alike.
Norfolk
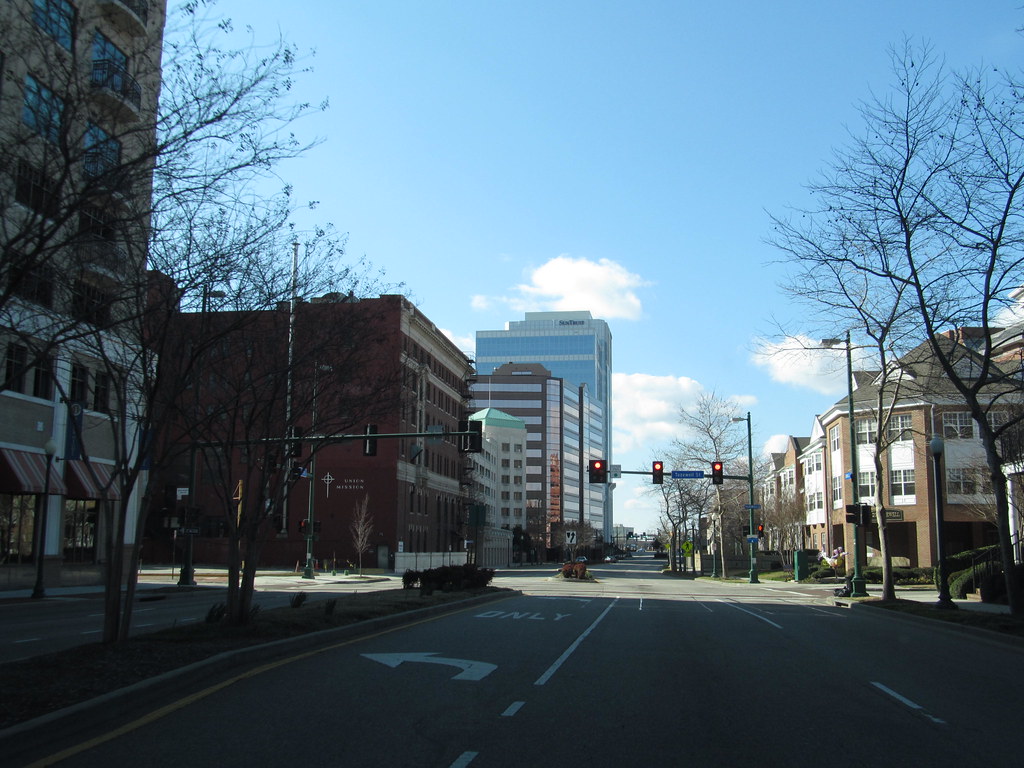

Norfolk is a bustling independent city located in Virginia, United States. As of the 2020 census, Norfolk had a population of 238,005, making it the third-most-populous city in Virginia after neighboring Virginia Beach and Chesapeake, and the 94th-largest city in the nation.
Norfolk is strategically located as the historical, urban, financial, and cultural center of the Hampton Roads region, which has more than 1.8 million inhabitants and is the 37th-largest metropolitan area in the US, with ten cities. The city was incorporated in 1705 and is bordered to the west by the Elizabeth River and to the north by the Chesapeake Bay. Norfolk shares land borders with the independent cities of Chesapeake to its south and Virginia Beach to its east.
With its extensive coastline along multiple bodies of water, Norfolk boasts many miles of riverfront and bayfront property, including beaches on the Chesapeake Bay. The city is also home to the largest naval base in the world, Naval Station Norfolk, as well as one of NATO’s two Strategic Command headquarters. Additionally, Norfolk is an important contributor to the Port of Virginia and is home to Maersk Line, Limited, which manages the world’s largest fleet of US-flag vessels.
With its rich history as a strategic military and transportation point, Norfolk is linked to its neighbors by an extensive network of interstate highways, bridges, tunnels, and three bridge-tunnel complexes.
Petersburg
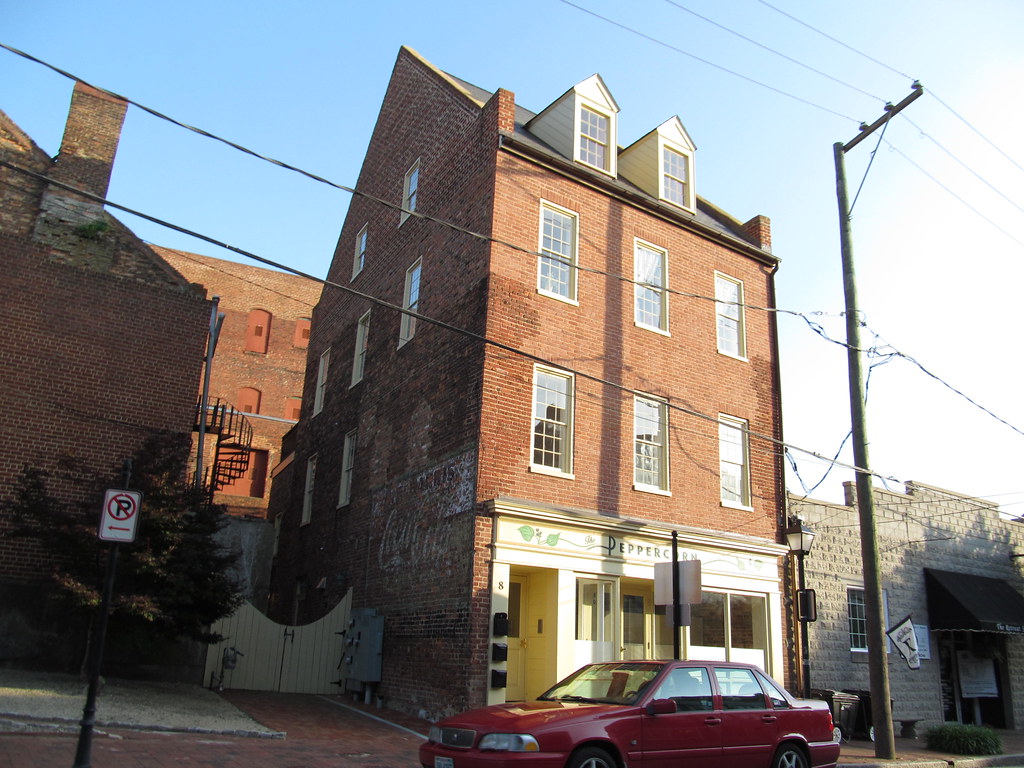

Petersburg is a vibrant independent city located in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 33,458 with a majority African American. The Bureau of Economic Analysis combines Petersburg (along with the city of Colonial Heights) with Dinwiddie County for statistical purposes.
The city is located 21 miles (34 km) south of the commonwealth (state) capital city of Richmond. Petersburg is situated at the fall line, which is the head of navigation of rivers on the U.S. East Coast, of the Appomattox River, a tributary of the larger James River that flows east to meet the southern mouth of the Chesapeake Bay at the Hampton Roads harbor and the Atlantic Ocean.
The Virginia House of Burgesses ordered Fort Henry built in 1645, which attracted traders and settlers to the area. The Town of Petersburg, chartered by the Virginia legislature in 1784, incorporated three early settlements, and in 1850 the legislature elevated it to city status. Petersburg grew as a transportation hub and developed a strong industry. It was the final destination on the Upper Appomattox Canal Navigation System, which opened in 1816, to a city mostly rebuilt after a devastating 1815 fire.
The city’s industries and transportation combined to make it the state’s second-largest city (after Richmond) by 1860. During the American Civil War, Petersburg became critical to Union plans to capture the Confederate States national capital established early in the war at Richmond due to its railroad network. The 1864–65 Siege of Petersburg, which included the Battle of the Crater and nine months of trench warfare, devastated the city.
Petersburg rebuilt its railroads, including a connecting terminal by 1866, although it never quite regained its economic position because much shipping traffic would continue to the Norfolk seaport. Today, both the CSX and Norfolk Southern railway networks serve Petersburg and battlefield sites are partly preserved as Petersburg National Battlefield by the National Park Service of the U.S. Department of the Interior.
Portsmouth

Portsmouth is a wonderful independent city located in southeast Virginia, United States. It lies across the Elizabeth River from Norfolk and is part of the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. As of the 2020 census, the population was 97,915, making it the 9th-most populous city in Virginia. Portsmouth is home to the historic and active U.S. Navy facility, the Norfolk Naval Shipyard.
The shipyard has been in operation since 1767 and has played a significant role in the country’s naval history. Today, it is one of the largest shipyards in the world, specializing in repairing and overhauling submarines and ships for the U.S. Navy.
The city of Portsmouth is also known for its rich history and cultural attractions, including the Portsmouth Art & Cultural Center, the Children’s Museum of Virginia, and the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard Museum. With its beautiful waterfront location and vibrant community, Portsmouth is a great place to visit and call home.
Richmond

Richmond is a historic and exciting capital city located in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Incorporated in 1742, Richmond has been an independent city since 1871. The city’s population in the 2020 census was 226,610, making it Virginia’s fourth-most populous city. Richmond is located at the James River’s fall line, surrounded by Henrico and Chesterfield counties, and is at the intersection of several major highways including Interstate 95 and Interstate 64.
The city has a rich history, having been an important village in the Powhatan Confederacy and the capital of the Colony and Dominion of Virginia in 1780. During the Revolutionary War and the American Civil War, Richmond played significant roles in the country’s history.
Today, Richmond’s economy is primarily driven by law, finance, and government, with the downtown area home to federal, state, and local governmental agencies as well as notable legal and banking firms. The greater metropolitan area includes several Fortune 500 companies, and the city is home to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 4th Circuit and a Federal Reserve Bank.
Roanoke

Roanoke is a marvelous independent city located in Southwest Virginia along the Roanoke River, in the Blue Ridge range of the greater Appalachian Mountains. At the 2020 census, Roanoke’s population was 100,011, making it the largest city in Virginia west of the state capital Richmond. It is the principal municipality of the Roanoke metropolitan area, which had a 2020 population of 315,251.
The Roanoke Valley was originally home to members of the Siouan-speaking Tutelo tribe, but Scotch-Irish and later German-American farmers gradually drove those Native Americans out of the area as the American frontier pressed westward. A significant turning point in the area’s history came in 1882 when the Norfolk and Western Railway (N&W) chose the small town of Big Lick as the site of its corporate headquarters and railroad shops.
Within two years, the town had become the City of Roanoke. Today, Roanoke is known for the Roanoke Star, an illuminated star that sits atop a mountain within the city’s limits and is the origin of its nickname “The Star City of the South”. The city’s location in the Blue Ridge Mountains provides access to numerous outdoor recreation opportunities, and the Roanoke Valley features 26 miles of greenways with bicycle and pedestrian trails.
Salem

Salem is a quaint independent city located in the U.S. Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 25,346. It is the county seat of Roanoke County, although the two are separate jurisdictions.
The city of Salem is combined with Roanoke County, which surrounds both Salem and the neighboring City of Roanoke, for statistical purposes. Salem has its own courthouse and sheriff’s office but shares a jail with Roanoke County, which is located in the Roanoke County Courthouse complex in Salem.
The city is home to Roanoke College, a private liberal arts college founded in 1842. Salem is also the home to a minor league baseball team, the Salem Red Sox, who play at the Haley Toyota Field. With its small-town charm and cultural attractions, Salem is a great place to visit and call home.
Staunton

Staunton is a charming independent city located in the U.S. Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 25,750. In Virginia, independent cities are separate jurisdictions from the counties that surround them, so the government offices of Augusta County are in Verona, which is contiguous to Staunton.
Staunton is a principal city of the Staunton-Waynesboro Metropolitan Statistical Area, which had a 2010 population of 118,502. The city is known for being the birthplace of Woodrow Wilson, the 28th U.S. president, and as the home of Mary Baldwin University, historically a women’s college.
The city is also home to Stuart Hall, a private co-ed preparatory school, as well as the Virginia School for the Deaf and Blind. Staunton was the first city in the United States with a fully defined city manager system, which it adopted in 1908. With its intriguing heritage and cultural hotspots, Staunton will welcome you with open arms.
Suffolk

Suffolk is a thriving independent city located in Virginia, United States. As of 2022, the population was 99,179, making it the 8th-most populous city in Virginia and the largest city in Virginia by boundary land area as well as the 14th-largest in the country.
Suffolk is located in the Hampton Roads metropolitan area, which includes the independent cities of Chesapeake, Hampton, Newport News, Norfolk, Portsmouth, and Virginia Beach, and smaller cities, counties, and towns of Hampton Roads.
With miles of waterfront property on the Nansemond and James rivers, present-day Suffolk was formed in 1974 after consolidating with Nansemond County and the towns of Holland and Whaleyville. The city is led by Mayor Mike Duman, who was elected in 2021. With its thriving economy, beautiful waterfront views, and rich history, Suffolk is a rewarding place to visit and call home.
Virginia Beach
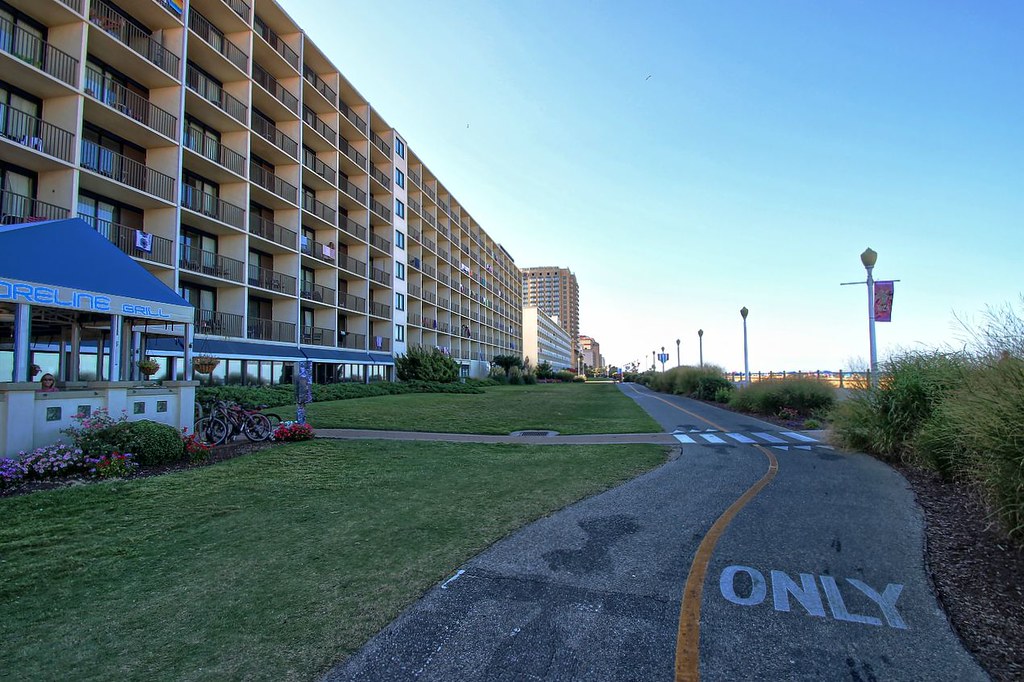

Virginia Beach is an exciting independent city located on the southeastern coast of Virginia, United States. The population was 459,470 at the 2020 census, making it the most populous city in Virginia, the fifth-most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, the ninth-most populous city in the Southeast, and the 42nd-most populous city in the U.S.
Located on the Atlantic Ocean at the mouth of the Chesapeake Bay, Virginia Beach is the largest city in the Hampton Roads metropolitan area which includes 6 other cities. This area, sometimes referred to as “America’s First Region”, also includes the independent cities of Chesapeake, Hampton, Newport News, Norfolk, Portsmouth, and Suffolk, as well as other smaller cities, counties, and towns of Hampton Roads.
Virginia Beach is a resort city with miles of beaches and hundreds of hotels, motels, and restaurants along its oceanfront. The city hosts the East Coast Surfing Championships as well as the Something in the Water music festival. It is also home to several state parks, military bases, and numerous historic sites.
Cape Henry, located near the point where the Chesapeake Bay and the Atlantic Ocean meet, was the site of the first landing of the English colonists, who eventually settled in Jamestown, on April 26, 1607.
The city is listed in the Guinness Book of Records as having the longest pleasure beach in the world and is located at the southern end of the Chesapeake Bay Bridge-Tunnel, which was the world’s longest bridge-tunnel complex until the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge opened in 2018. With its beautiful beaches, rich history, and absorbing culture, Virginia Beach is a wonderful destination to visit.
Waynesboro
![Virginia Map With Cities and Highways: Easy Exploration 25 Downtown Waynesboro, Virginia [01]](https://live.staticflickr.com/65535/49550992253_0c9f4c278f_b.jpg)
Waynesboro is an appealing independent city located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. Formerly known as Flack, it is a principal city of the Staunton-Waynesboro Metropolitan Statistical Area. Waynesboro is located in the picturesque Shenandoah Valley and is surrounded by Augusta County.
As of the 2020 census, the population was 22,196, making it a small but vibrant community. The city is known for its beautiful mountain views, historic downtown area, and outdoor recreational opportunities. With its small-town charm and natural beauty, Waynesboro attracts residents and visitors from all over the area.
Williamsburg
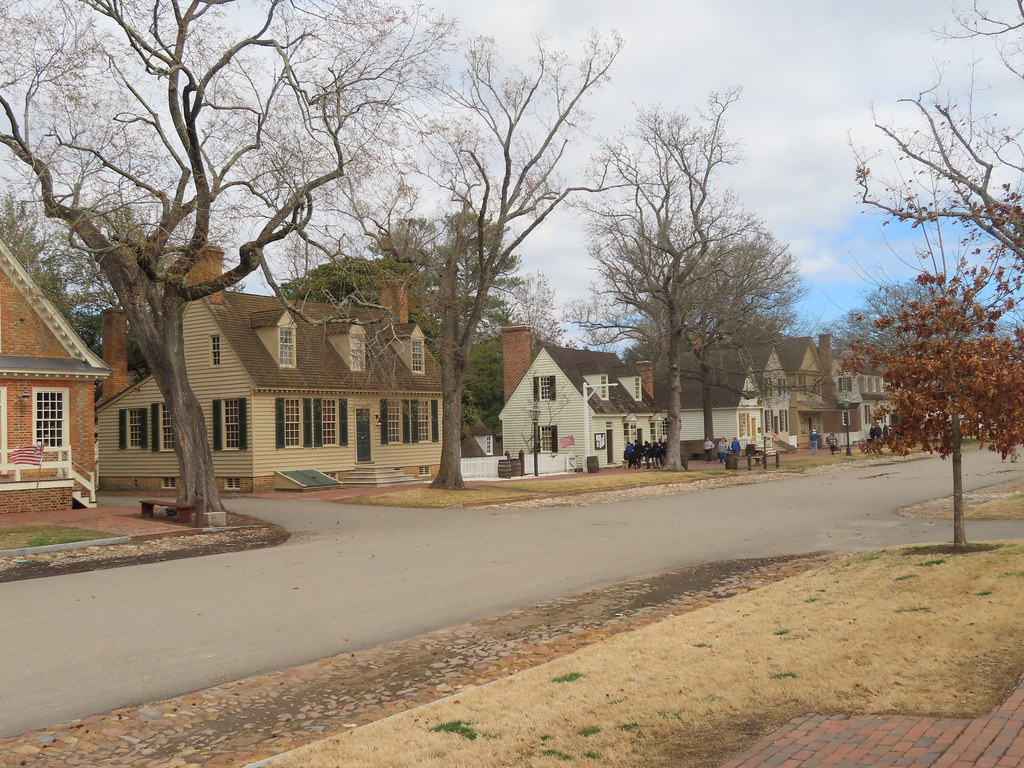

Williamsburg is a historic independent city located in Virginia, United States. As of the 2020 census, it had a population of 15,425. Located on the Virginia Peninsula, Williamsburg is in the northern part of the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. The city was founded in 1632 as Middle Plantation, a fortified settlement on high ground between the James and York rivers.
It served as the capital of the Colony and Commonwealth of Virginia from 1699 to 1780 and became the center of political events in Virginia leading to the American Revolution. The College of William & Mary, established in 1693, is the second-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and the only one of the nine colonial colleges in the South.
The city’s tourism-based economy is driven by Colonial Williamsburg, the city’s restored Historic Area. Along with nearby Jamestown and Yorktown, Williamsburg forms part of the Historic Triangle, which annually attracts more than four million tourists. Modern Williamsburg is also a college town, inhabited in large part by William & Mary students, faculty, and staff. With its rich history and cultural attractions, Williamsburg is a delightful place to visit and learn about the nation’s early history.
Winchester

Winchester is a scenic independent city located in the northwesternmost part of the Commonwealth of Virginia, United States. It is the county seat of Frederick County, although the two are separate jurisdictions. As of the 2020 census, the city’s population was 28,120.
Winchester is the principal city of the Winchester metropolitan area extending into West Virginia, which is a part of the Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area. The city is known for its lovely downtown area, historic architecture, and outdoor recreational opportunities.
Winchester is home to Shenandoah University, a private liberal arts university founded in 1875, as well as the Museum of the Shenandoah Valley, which showcases the region’s rich history and culture.
Interstates
Interstate 77

Interstate 77 (I-77) is a vital north-south Interstate Highway in the US state of Virginia, stretching for 67 miles (108 km) and serving the towns of Hillsville, Wytheville, and Bland. It runs parallel to US Route 52 (US 52) and passes through the Big Walker Mountain Tunnel and East River Mountain Tunnel, which is located on the West Virginia state line and is one of only two land vehicular tunnels to cross a state line.
I-77 provides an important transportation link for both commuters and commercial traffic, connecting Virginia with West Virginia and other parts of the country. With its expansive mountain views and unique tunnels, I-77 is a popular route for travelers in Virginia.
Interstate 81

Interstate 81 (I-81) is a major north-south Interstate Highway that stretches for 855.02 miles (1,376.02 km) across the eastern United States. In Virginia, I-81 covers a distance of 324.92 miles (522.91 km), making it the longest portion of the route within any state.
It runs from the Tennessee state line near Bristol to the West Virginia state line near Winchester, passing through the cities of Bristol, Roanoke, Lexington, Staunton, and Harrisonburg along the way. I-81 is an important transportation corridor for both commercial and passenger traffic, connecting Virginia with other parts of the country. With its scenic mountain views and convenient access to major cities, I-81 is a brilliant route for travelers in Virginia.
Interstate 85

Interstate 85 (I-85) is a vital part of the Interstate Highway System that runs from Montgomery, Alabama, to Petersburg, Virginia. In Virginia, I-85 covers a distance of 68.64 miles (110.47 km), stretching from the North Carolina state line near Bracey north to I-95 in Petersburg. The highway passes through the eastern part of Southside, where it runs parallel to US Route 1 (US 1) from Petersburg, where it runs concurrently with US 460, to the south of South Hill, where it intersects with Southside’s major east-west highway, US 58.
I-85 is an important transportation link for connecting the Greater Richmond Region with the Research Triangle and other major metropolitan areas of North Carolina. As a mainline Interstate Highway, I-85 is a part of the National Highway System for its entire length in Virginia. With its convenient access to major cities and regional hubs, I-85 is a popular route for both commercial and passenger traffic in Virginia.
Interstate 95

Interstate 95 (I-95) is a crucial highway that runs for 179 miles (288 km) within the Commonwealth of Virginia, connecting its borders with North Carolina and Maryland. It intersects with I-85 in Petersburg and is concurrent with I-64 for three miles (4.8 km) in Richmond. Originally planned as a highway through Washington, D.C., I-95 was rerouted along the eastern portion of the Capital Beltway concurrent with I-495.
The route passes through several medium-sized cities, including Emporia, Petersburg, Colonial Heights, Fredericksburg, and Alexandria. The stretch of I-95 between Fredericksburg and Springfield is known for being one of the most congested routes of highway in the US, particularly during holidays and rush hours. To alleviate this problem, the Virginia Department of Transportation (VDOT) is widening I-95 to six lanes between the cities, adding express lanes, and new offramps to US Route 17 (US 17) and State Route 3 (SR 3) through Fredericksburg.
On January 4, 2022, a major traffic jam occurred due to heavy snowfall, leaving some people stuck in traffic for more than 24 hours. Despite occasional challenges, I-95 remains a vital transportation link for both commercial and passenger traffic in Virginia.
Interstate 64

Interstate 64 (I-64) is a crucial east-west highway that runs for 299 miles (481 km) through the middle of Virginia, connecting West Virginia to the Hampton Roads region. It passes through several major cities, including Lexington, Staunton, Charlottesville, Richmond, Newport News, Hampton, and Norfolk.
I-64 is notable for crossing the mouth of the harbor of Hampton Roads on the Hampton Roads Bridge Tunnel (HRBT), the first bridge tunnel to incorporate artificial islands, concurrent with U.S. Route 60 (US 60). Another noteworthy section is through Rockfish Gap, a wind gap in the Blue Ridge Mountains, which features an innovative system of airport-style runway lighting embedded into the pavement to aid motorists during periods of poor visibility due to fog or other conditions.
I-64 is a vital transportation link for both commercial and passenger traffic in Virginia, connecting major cities and regions across the state. With its scenic views and innovative infrastructure, I-64 is a popular route for travelers in Virginia.
Interstate 66

Interstate 66 (I-66) begins at a directional T interchange with I-81 near Middletown, Virginia, and heads east as a four-lane freeway. It meets US 522/US 340 at a partial cloverleaf interchange, with the two routes heading south to Front Royal and north to Lake Frederick.
I-66 continues to parallel SR 55 (John Marshall Highway) and meets US 17 at a partial interchange with no access from southbound US 17 to westbound I-66. SR 55 merges onto the freeway at this interchange, forming a three-way concurrency that ends near Marshall. Expanding to six lanes, I-66 enters the towns of Haymarket and Gainesville, reaching interchanges with US 15 and US 29 in each town, respectively.
The highway then passes to the south of the Manassas National Battlefield Park and to the north of the Bull Run Regional Park. I-66 has a tolled high-occupancy vehicle lane (HO/T lane) from US 15 to the Capital Beltway, providing access to D.C. suburbs. With its convenient access to major cities and suburbs, I-66 is an important transportation link for both commercial and passenger traffic in Virginia.
Highways
Route 1

U.S. Route 1 (US 1) is a significant north-south U.S. Route that serves the East Coast of the United States. In Virginia, US 1 runs north-south through South Hill, Petersburg, Richmond, Fredericksburg, and Alexandria, connecting North Carolina to the 14th Street bridges into the District of Columbia.
It is completely paralleled by Interstate Highways in Virginia – I-85 south of Petersburg, I-95 north to Alexandria, and I-395 into the District of Columbia – and now serves mainly local traffic. US 1 was initially part of prior Virginia state routes, primarily State Route 31 (SR 31), and earlier than that, it was part of an auto trail known as the Jefferson Davis Highway.
While minor adjustments have been made, it still largely follows the same route it has since first being designated in 1926. At its north end, on the approach to the 14th Street bridges, US 1 is concurrent with I-395, and the rest of US 1 is on surface roads. US 1 is an important transportation link for local traffic in Virginia, connecting several major cities and regions.
Route 11

U.S. Route 11 (US 11) is a significant north-south United States Numbered Highway in western Virginia, spanning 339 miles (546 km) and making it the second longest numbered route (after US 58) and the longest primarily north-south route in the state. It enters Virginia from Tennessee as the divided routes US 11E and US 11W at Bristol, closely following the West Virginia border through the Blue Ridge Mountains and Shenandoah Valley before entering the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia from Frederick County.
Most of the route parallels I-81 and serves several cities and towns, including Bristol, Abingdon, Wytheville, Christiansburg, Roanoke, Lexington, Staunton, Harrisonburg, Strasburg, and Winchester. US 11 was first designated through Virginia in 1926 and has largely followed the same route since.
Prior to the construction of the Interstate Highway System, it was the primary long-distance route for traversing the western part of the state, roughly following the Great Wagon Road, a colonial-era road that followed the Appalachian Mountains from Georgia to Pennsylvania. With its scenic views and historical significance, US 11 is a popular route for travelers in western Virginia.
Route 13

U.S. Route 13 (US 13) is a significant north-south United States Numbered Highway that was established in 1926 and runs for 518 miles (834 km), from Interstate 95 (I-95) just north of Fayetteville, North Carolina, north to US 1 in Morrisville, Pennsylvania, a northeastern suburb of Philadelphia.
In Virginia, US 13 runs north-south through the Hampton Roads and Eastern Shore regions of the state, utilizing the Chesapeake Bay Bridge Tunnel to get between the two. In the Hampton Roads area, it uses the Military Highway to bypass the city centers. US 13 is usually a four-lane highway, sometimes up to freeway or expressway standards with controlled access.
With its convenient access to the major cities and regions of Virginia, US 13 is an important transportation link for both commercial and passenger traffic. The Chesapeake Bay Bridge Tunnel, which is part of the US 13 route, is a popular scenic attraction in Virginia.
Route 15

U.S. Route 15 (US 15) is a significant part of the United States Numbered Highway System, running from Walterboro, South Carolina, to Painted Post, New York. In Virginia, US 15 spans 230.37 miles (370.74 km), running from the North Carolina state line near Clarksville north to the Maryland state line at the Potomac River near Lucketts.
US 15 is a major north-south highway through the Piedmont of Virginia, connecting Clarksville and Farmville in Southside with Culpeper, Warrenton, and Leesburg in Northern Virginia. With its convenient access to several major cities and regions in Virginia, US 15 is an important transportation link for both commercial and passenger traffic. The route also offers expansive views of the Piedmont region of Virginia, making it a popular route for travelers.
Route 17

U.S. Route 17 (US 17) is a significant part of the United States Numbered Highway System, running from Punta Gorda, Florida, to Winchester, Virginia. In Virginia, US 17 spans 255.83 miles (411.72 km), running from the North Carolina state line in Chesapeake north to its northern terminus at US 11, US 50, and US 522 in Winchester.
US 17 is a major highway in the eastern half of Virginia, connecting the Albemarle Region of North Carolina with the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. Within the urban area, US 17 passes through the South Hampton Roads cities of Chesapeake, Portsmouth, and Suffolk, as well as the Virginia Peninsula city of Newport News. Between Yorktown and Fredericksburg, the highway serves as the primary route of the Middle Peninsula.
At Fredericksburg, US 17 leaves the Atlantic Plain and passes through the Piedmont town of Warrenton before crossing the Blue Ridge Mountains on its way to Winchester in the Shenandoah Valley. The route from Tappahannock to Winchester roughly follows the Confederate march during the Civil War to Gettysburg, offering a glimpse into Virginia’s rich history.
Route 19

U.S. Route 19 (US 19) is a significant part of the United States Numbered Highway System, running from Memphis, Florida, to Erie, Pennsylvania. In Virginia, the highway spans 88.89 miles (143.05 km) between two pairs of twin cities: Bristol, Tennessee, and Bristol, Virginia, at the Virginia-Tennessee state line, and Bluefield, Virginia, and Bluefield, West Virginia, at the Virginia-West Virginia state line.
US 19 has lengthy concurrencies with US 11, US 58 Alternate (US 58 Alt.), and US 460 during its course, connecting Abingdon, Lebanon, and Tazewell within Washington, Russell, and Tazewell counties in Southwest Virginia.
With its convenient access to several cities and regions in Virginia, US 19 is an important transportation link for both commercial and passenger traffic. The highway also offers sweeping views of the Appalachian Mountains, making it a popular route for travelers in Southwest Virginia.
Route 21
U.S. Route 21 (US 21) is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that travels through several states, including Virginia. After crossing the state line, US 21 reaches the town of Independence, where it splits with US 221 and continues north. The route goes through the Mount Rogers National Recreation Area, offering clear views of the Appalachian Mountains, before entering the city of Wytheville.
After a short concurrency with US 11 in downtown Wytheville, US 21 goes north and ends at the intersection of I-81/US 52. US 21 travels 35 miles (56 km) through western Virginia, mostly as a two-lane rural mountain road. With its beautiful views and rural charm, US 21 is a popular route for travelers looking to explore the natural beauty of western Virginia.
Route 29

U.S. Route 29 (US 29) is a major north-south route in the Commonwealth of Virginia, spanning 248 miles (399 km) from the North Carolina border at the city of Danville to the Key Bridge in Washington, D.C. US 29 roughly bisects Virginia into eastern and western halves, providing one of the major north-south routes through the Commonwealth.
Much of US 29 in Virginia is known as the Seminole Trail, and in Northern Virginia, it is known as Lee Highway, except in Falls Church, where it acts as the east/west divider for city streets and is called North or South Washington Street, and Arlington, where it was renamed Langston Boulevard in July 2021 in honor of John Mercer Langston.
The entire length of US 29 from the North Carolina border to the Potomac River is officially designated as the “29th Infantry Division Memorial Highway” in honor of the Army unit that played a significant role in the liberation of France during World War II.
For most of its route through Virginia, US 29 has been constructed to be at least four lanes along its route, with some exceptions where it passes through parks or counties. The highway also has eleven bypass routes around various cities and towns, providing convenient access for both commercial and passenger traffic.
Route 33

U.S. Route 33 (US 33) is a significant part of the U.S. Highway System, running from Elkhart, Indiana to Richmond, Virginia. In Virginia, the U.S. Highway spans 135.60 miles (218.23 km), running from the West Virginia state line near Rawley Springs east to its eastern terminus at SR 33 in Richmond.
US 33 is the primary east-west highway of Rockingham County, connecting the independent city of Harrisonburg (which also serves as the seat of Rockingham County), the town of Elkton, and an entrance to Shenandoah National Park. East of the Blue Ridge Mountains, US 33 connects the Piedmont communities of Stanardsville, Gordonsville, and Louisa.
The U.S. Highway is also a major suburban and urban route in the Richmond metropolitan area, running concurrently with US 250 within the city. SR 33 continues from US 33’s eastern terminus as a state-numbered extension of the U.S. Highway that connects Richmond with Virginia’s Middle Peninsula.
With its convenient access to several cities and regions in Virginia, US 33 is a vital transportation link for both commercial and passenger traffic. The highway also offers dramatic views of the Shenandoah Valley and the Piedmont region of Virginia, making it a wonderful choice for travelers.
Route 50

U.S. Route 50 (US 50) is a chief transcontinental highway that stretches from Ocean City, Maryland to West Sacramento, California. In the state of Virginia, US 50 covers 86 miles (138 km) from the border with Washington, D.C. at a Potomac River crossing at Rosslyn in Arlington County to the West Virginia state line near Gore in Frederick County.
The highway serves as a major east-west route through Northern Virginia, connecting several cities and towns, including Arlington, Fairfax, and Winchester. US 50 also passes through the Shenandoah Valley, offering pleasing views of the Appalachian Mountains and several historic landmarks.
With its convenient access to several cities and regions in Virginia, US 50 is an important transportation link for both commercial and passenger traffic. The highway also serves as a popular route for travelers looking to explore the natural landscapes and rich history of Virginia.

